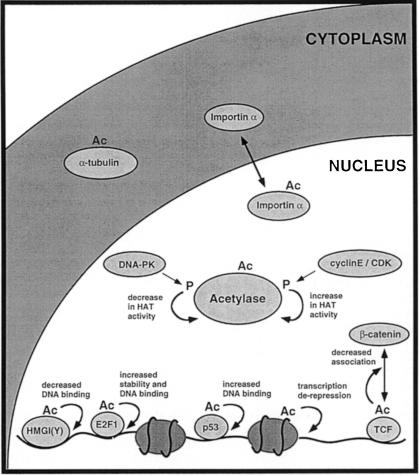
Fig. 1. Acetylation of a variety of proteins by acetylases affects their activity in different ways. The activity of acetylases is regulated, at least in vitro, by kinases involved in DNA repair (DNA–PK) and cell cycle progression (cyclin E–CDK). Acetylated targets include histones, nuclear acetylases (P/CAF and p300), transcription factors [e.g. HMGI(Y), E2F1, p53 and TCF], the nuclear import factor, importin-α and α–tubulin. Acetylation has many consequences, including effects on DNA binding, protein stability and protein–protein interaction. Ac, acetylation; p, phosphorylation.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.