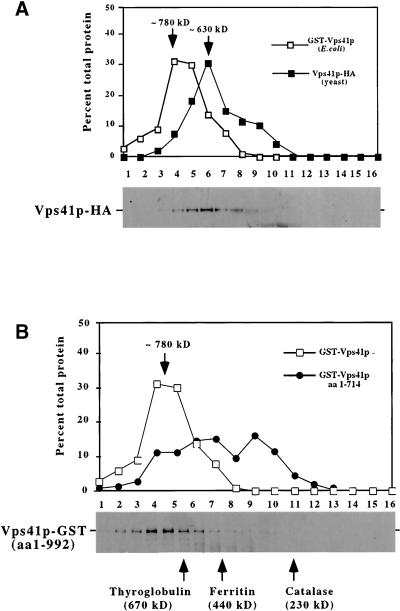
Figure 6.
Analysis of Vps41p oligomeric complex. (A) Lysates were made from 100 OD600 equivalents of wild-type yeast expressing an integrated VPS41-HA fusion construct (DKY25) and centrifuged at 100,000 × g to remove insoluble proteins and membranes. The supernatant fraction was applied to the S300 sizing column. Proteins in the fractions were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies against the HA epitope. The yeast Vps41p-HA profile is compared with recombinantly produced GST-Vps41p. (B) GST fused to either full-length Vps41p (pGSTVPS41) or a truncated form of Vps41p containing amino acids 1–714 (pGSTVPS41T) were induced in E. coli (XLIB). Lysates were made from 20 OD600 equivalents of E. coli and centrifuged at 100,000 × g to remove insoluble proteins and membranes. Supernatant fractions for both GST-Vps41p and GST-Vps41p (aa 1–714) truncation were subjected to fractionation on S300 sizing columns. In both A and B, the relative amounts of proteins in each fraction from the columns were compared using Scion Image 1.62 and plotted as a percentage of total protein. Bottom panels: Western blots of Vps41p-HA (A) and GST-Vps41p (B) from the columns. Arrows indicate the approximate size of the peak fractions in both A and B.