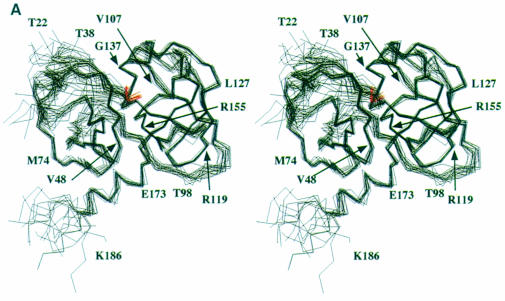
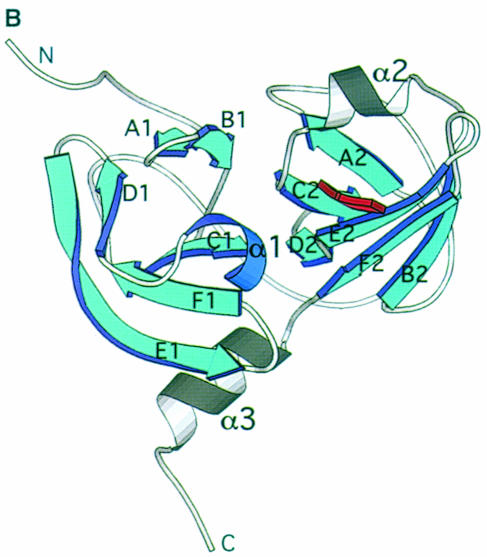
Fig. 2. (A) Stereoview of the 20 minimum energy structures. The superposition has been obtained using the structurally conserved regions (SCRs) as defined previously in Barbato et al. (1999). The inhibitor α–C atoms are shown in red. The N–terminal 21 residues were not included in the structure calculations, since their conformation is ill defined. (B) Molscript (Kraulis, 1991) representation of the NS3 protease domain, the chymotrypsin-like common SCRs are coloured in blue and the structural element labels follow the chymotrypsin-like nomenclature. The residues forming the secondary structural elements are: strands A1 (34–37), B1 (41–44), C1 (51–55), D1 (63–66), E1 (69–78), F1 (82–86), A2 (104–108), B2 (122–126), C2 (141–145), D2 (150–152), E2 (155–159), F2 (166–170); helices α1 (55–59), α2 (132–136), α3 (173–180).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.