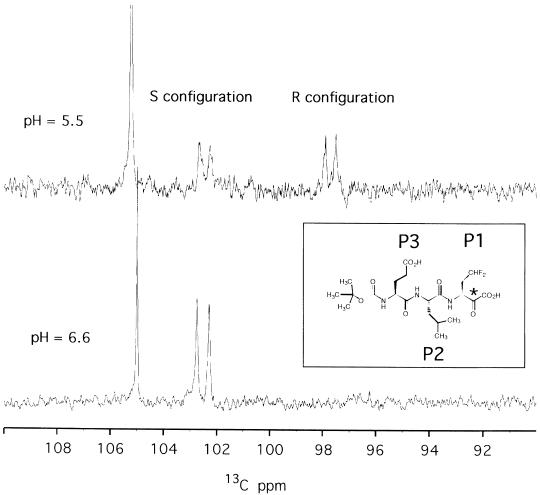
Fig. 3. The inset shows the reversible covalently bound inhibitor α–ketoacid Boc-Glu-Leu-(γdi-fluoro)Abu; the corresponding positions in the substrate-like nomenclature (P1, P2 and P3) are also indicated. The asterisk labels the activated carbonyl moiety, which acts as binding group and becomes the hemiketal chiral carbon upon complex formation. The spectra show regions of the 1D 13C experiment where the hemiketal carbon of the complex resonates. At pH 6.6 (bottom) only one doublet resonance is visible at 102.6 p.p.m., corresponding to the S configuration; at pH 5.5 (top), two resonances of similar intensity appear at 102.6 and 97.6 p.p.m. for the R and S configurations, respectively. The hemiketal signals are doublets since they are coupled with the α–C, which is also 13C labelled, while the carboxyl atom is unlabelled. The intense singlet at ∼105 p.p.m. represents a buffer resonance.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.