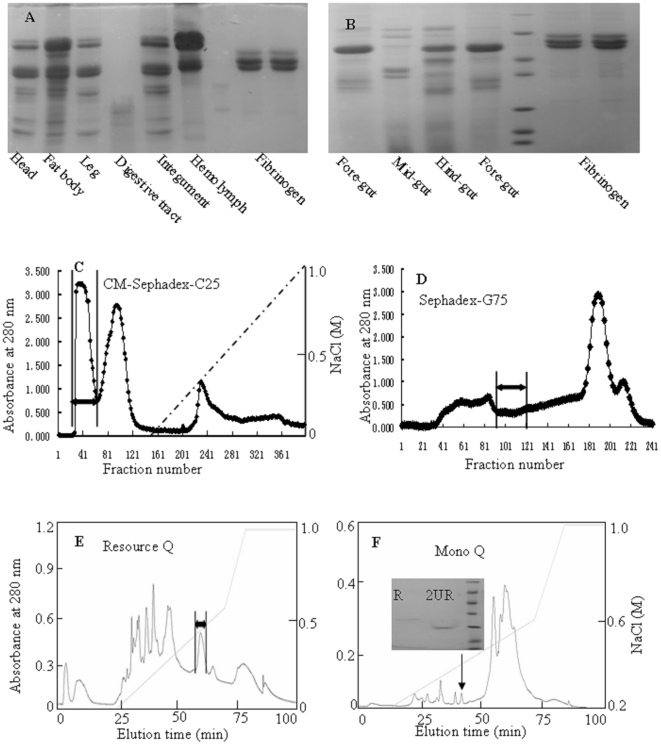
Figure 1. Purification of fibriongenolytic molecules from mid-guts of E. sinensis.
A and B: tissues extrats from legs, integuments, fat bodies, heads, digestive tracts and hemolymph of E. sinensis were used to test their thrombolytic abilities against fibrinogen. 5 µg total extracted protein was incubated with 20 µg fibrinogen for 10 h at 37°C and subjected reduced SDS-PAGE analysis in a gel concentration of 15%. C: cationic exchange chromatography of aliquot of 1.0 g MGS by CM-Sephadex C-25 (Amersham Biosciences, 2.6×40 cm). The interesting peak was indicated by an arrow. D: the collected fraction containing fibrinogenolytic activity from “C” was subjected to Sephadex G-75 gel filtration (Amersham Biosciences, superfine, 2.6×100 cm), the elution was performed by 0.1 M Tris-HCl pH 7.8 with a flow rate of 0.3 ml/min. E: The collected fraction from “D” was subjected to AKTA FPLC Resource Q (1 ml volume, Amersham Biosciences) anionic exchange equilibrated with 0.02 M Tris-HCl pH 7.8. The elution was performed at a flow rate of 1 ml/min with the indicated NaCl gradient. F: the collected fraction from “E” was subjected to AKTA FPLC Mono Q (1 ml volume, Amersham Biosciences) anionic exchange equilibrated with 0.02 M Tris-HCl pH 8.3. The elution was performed at a flow rate of 1 ml/min with the indicated NaCl gradient. The purified protein containing fibrinogenolytic activity was indicated by an arrow. Inset in Fig. 1F: SDS-PAGE analysis of purified protein as indicated in Fig. 1F in 15% gel concentration. R: reduced; UR: Unreduced.