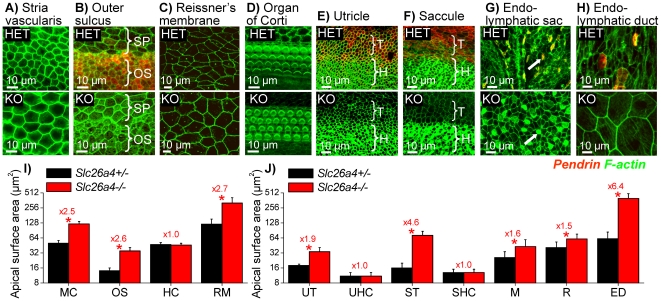
Figure 7. Epithelial cell stretching in the cochlea and the vestibular labyrinth at P2.
Pendrin (red) was visualized by immunocytochemistry and F-actin (green) was labeled in Slc26a4+/− (HET) mice and Slc26a4−/− (KO) mice. A–D: Whole-mounts of epithelial cells from the cochlea. Abbreviations: SP, spiral prominence epithelial cells; OS, outer sulcus epithelial cells. E–H) Whole-mounts of epithelial cells from the vestibular labyrinth and endolymphatic sac. Mitochondria-rich cells in endolymphatic sac from Slc26a4+/− and Slc26a4−/− mice are marked by arrows. Abbreviations: T, transitional cells; H, hair cells. I: Summary of apical cell surface area measurements (avg±SD, N = 15) made on cochlea epithelial cells. Abbreviations: MC, marginal cells of stria vascularis; OS, outer sulcus epithelial cells; HC, hair cells; RM, Reissner's membrane epithelial cells. J: Summary of apical cell surface area measurements (avg±SD, N = 15) made on vestibular epithelial cells. Abbreviations: UT, utricular transitional cells; UHC, utricular hair cells; ST, saccular transitional cells; SHC, saccular hair cells; M, mitochondria-rich cells; R, ribosome-rich cells; ED, endolymphatic duct epithelial cells. Significant differences between Slc26a4+/− (black) and Slc26a4−/− (red) mice are marked with a star. Figures preceded by ‘x’ indicate the factor between measurements in Slc26a4+/− and Slc26a4−/− mice.