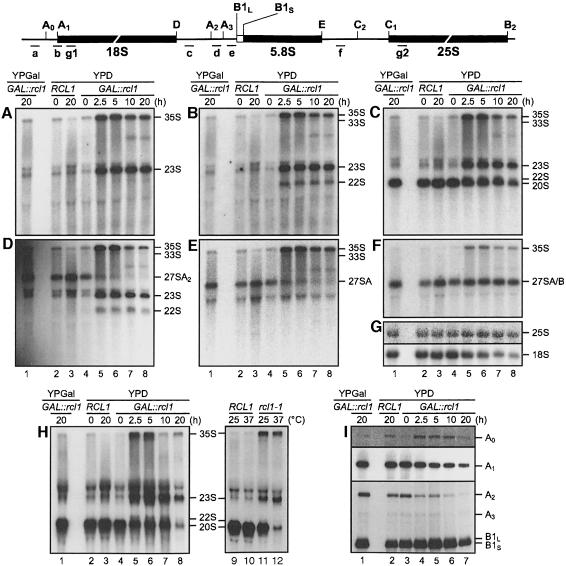
Fig. 6. Depletion or inactivation of Rcl1p affects pre-rRNA processing at sites A0, A1 and A2 (A–G and H, lanes 1–8). Northern analysis of pre-rRNAs accumulating in the wild-type strain grown in YPD (lanes 2 and 3) and GAL::rcl1 strain grown either in YPGal (lanes 1) or YPD (lanes 4–8). The following oligonucleotide probes (indicated schematically above the gels) were used: (A) probe a, the 5′ETS upstream of A0; (B) probe b, junction of 5′ETS and 18S rRNA; (C and H) probe c, the ITS1 upstream of A2; (D) probe d, between A2 and A3; (E) probe e, the ITS1 downstream of A3; (F) probe f, the ITS2 upstream of C2; (G) probes g1 and g2, complementary to 18S and 25S rRNA, respectively; (H) lanes 9–12, processing intermediates accumulating in the rcl1-1 ts mutant grown at permissive or restrictive temperature (37°C, 5 h). (I) Primer extension analysis of RNAs accumulating in the GAL::rcl1 strain grown either in YPGal (lane 1) or YPD (lanes 3–7), and in the wild-type strain grown in YPD (lane 2). Oligo g1 was used for primer extension to sites A0 and A1, and oligo f for extension to sites A2, A3 and B1L/S. Positions of primer extension stops corresponding to different pre-rRNA cleavage sites are indicated. The A0 and A1 panels represent different exposures of the same gel.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.