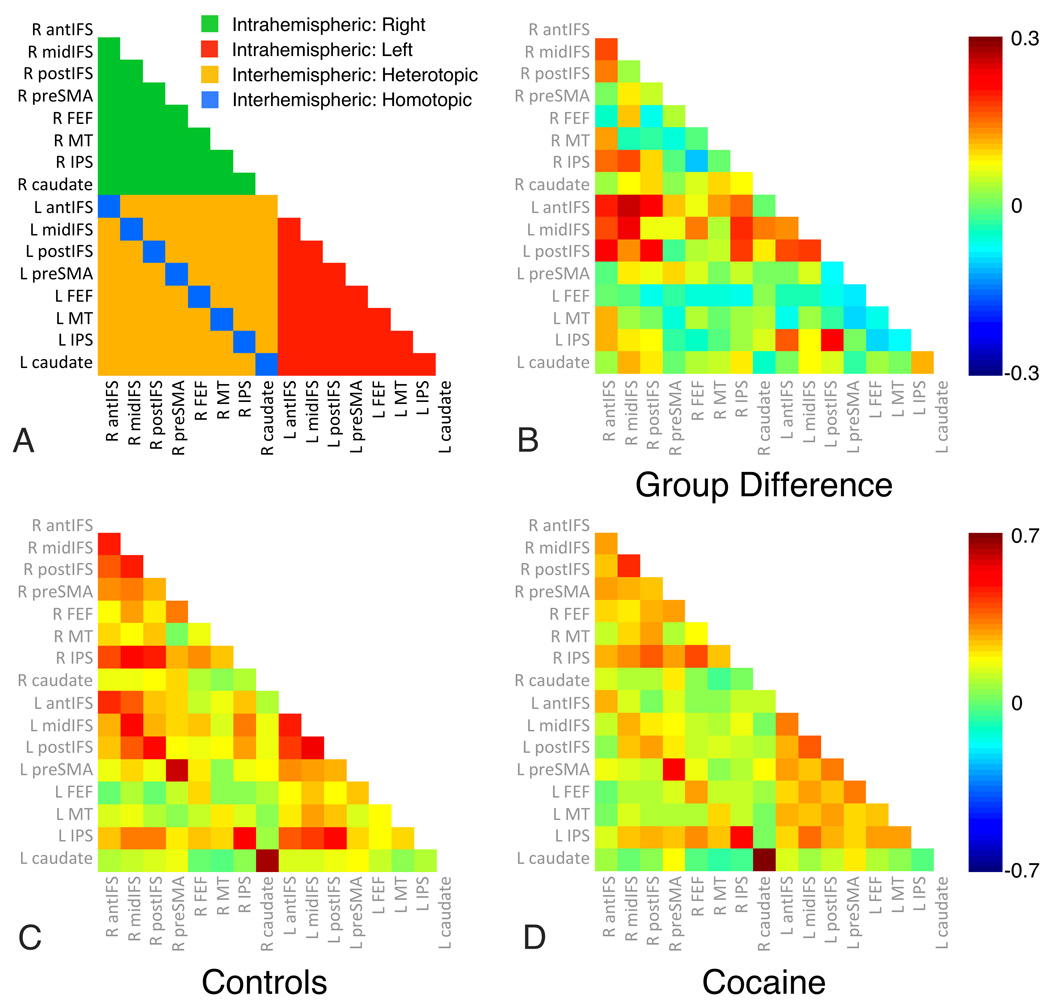
Figure 2. Cocaine-dependent participants exhibit reduced interhemispheric, but not intrahemispheric RSFC within the Dorsal Attention Network (DAN).
We tested for group differences in intrahemispheric (e.g., right IFS and right IPL), heterotopic interhemispheric (e.g., right IFS and left IPL) and homotopic interhemispheric (e.g., right and left IFS) RSFC between all pairs of 16 DAN nodes. Relative to controls, the cocaine-dependent group exhibited reduced homotopic (controls mean=0.45±0.11; cocaine mean=0.39±0.09; t(2,47)=2.66, p<0.05) and heterotopic (controls mean=0.16±0.07; cocaine mean=0.11±0.07; t(2,47)=2.68, p<0.05) interhemispheric RSFC, but not reduced intrahemispheric RSFC (controls left-left mean=0.25±0.07; cocaine left-left mean=0.23±0.08; t(2,47)=0.76, p=0.45; controls right-right mean=0.25±0.1; cocaine right-right mean=0.21±0.08; t(2,47)=1.44, p=0.16). Abbreviations: R: Right; L: Left; antIFS: anterior inferior frontal sulcus; midIFC: middle IFS; postIFS: posterior IFS; preSMA: presupplementary motor area; FEF: frontal eye fields; MT: middle temporal area; IPS: intraparietal sulcus.