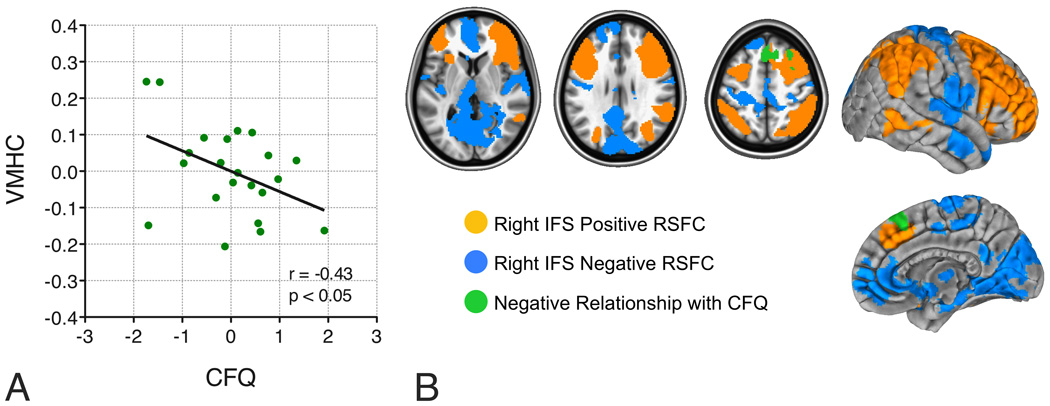
Figure 3. ROI-based and voxel-wise brain/behavior relationships.
A. Interhemispheric RSFC (i.e., VMHC) within a 4mm-radius sphere centered on the peak of the group difference in VMHC correlated with self-reported cognitive failures, as measured by the Cognitive Failures Questionnaire (CFQ; r=−0.43, n=23, p<0.05). Cocaine-dependent participants with the weakest prefrontal interhemispheric RSFC reported experiencing more frequent attentional failures. This relationship remained significant after adjusting for cocaine withdrawal symptoms (as measured by the Cocaine Selective Severity Assessment – CSSA: r=−0.66, p<0.001).
B. Voxel-wise analyses revealed relationships between right IFS RSFC and self-reported cognitive failures. Shown in green is the medial/superior lateral premotor area whose RSFC with right IFS exhibited a negative relationship with the CFQ. Cocaine-dependent participants with the weakest RSFC between these two areas reported experiencing more frequent attentional failures. Axial slices (z = 5; 28; and 51) are displayed according to neurological convention (right is right).