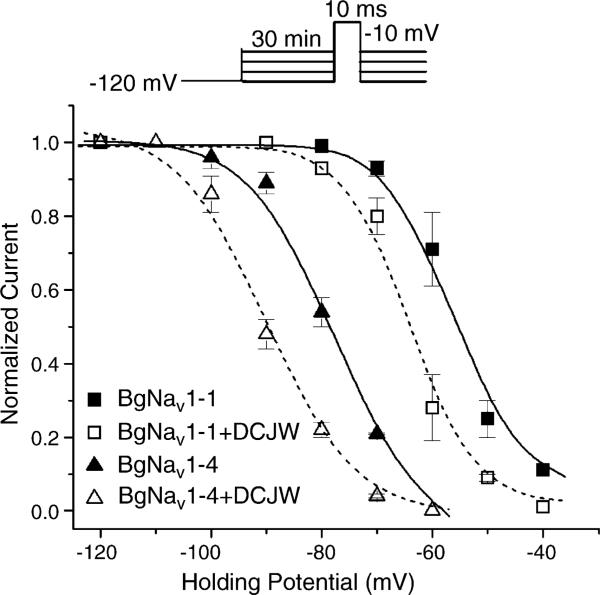
Fig. 2.
DCJW shifted the steady-state inactivation in the hyperpolarizing direction. For the control, peak current recorded at various holding potentials was normalized to the peak current recorded at the holding potential of −120 mV. For the DCJW treatment, peak currents recorded after 30 min of exposure to 20 μM DCJW at depolarizing holding potentials were normalized to the peak current at −120 mV in control. The data were fitted to the standard Boltzmann function. For BgNav1-4 in control: V0.5 = −77.8 ± 0.9 mV, k = 6.5 ± 0.8, and treated with DCJW: V0.5 = −90.0 ± 1.0 mV, k = 6.8 ± 1.0. For BgNav1-1 in control: V0.5 = −56.5 ± 0.5 mV, k = 4.5 ± 0.4 and treated with DCJW: V0.5 = −64.1 ± 0.9 mV, k = 4.3 ± 0.7. Each point represents data from four oocytes.