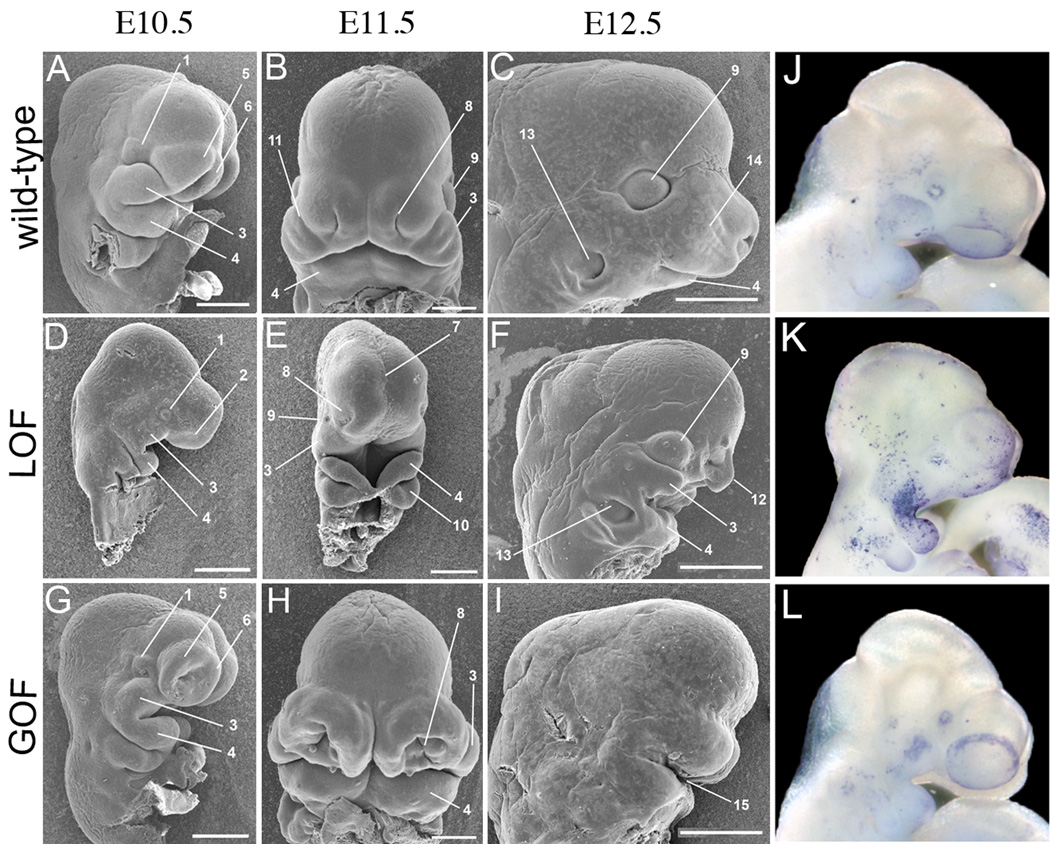
Figure 2. Conditional mutants exhibit complementary growth defects during craniofacial development.
Scanning electron microscopy images of wild-type (A–C), LOF (D–F) and GOF (G–I) embryos shown at E10.5 (A, D, G), E11.5 (B, E, H), and E12.5 (C, F, I). Images in B, E, & H are shown in a ventral view, all others are lateral views. J–L) Lateral views of E10.5 wild-type (J), LOF (K), and GOF (L) stained for cell death using TUNEL. e – eye, 1 – optic eminence, 2 – olfactory placode, 3 – maxillary prominence (upper jaw), 4 – mandibular prominence (lower jaw), 5 – lateral nasal process, 6 – medial nasal process, 7 – groove overlying the lamina terminalis of forebrain, 8 – nasal pit, 9 – eye, 10 – branchial arch two, 11 – lacro nasal groove, 12 – frontal nasal process, 13 – ear, 14 – vibrissae, 15 – oral cavity. Scale bars in C, F, & I represent 1mm, all others represent 500µm.