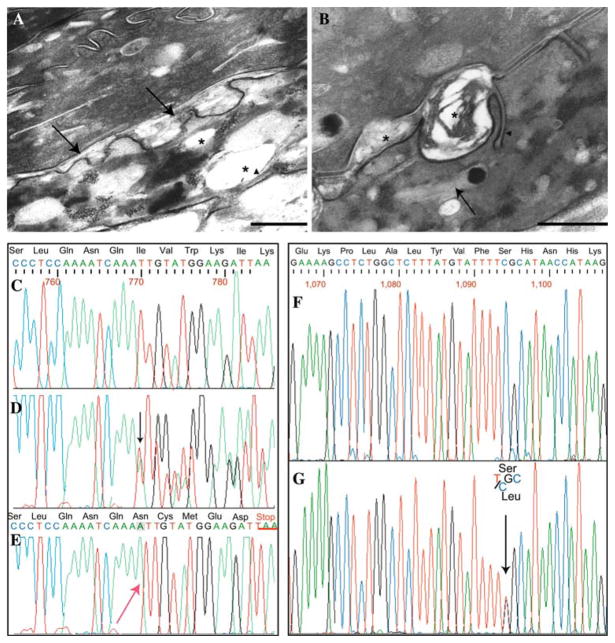
Fig. 1.
Electron micrographs from involved skin. a Membrane-bound electron-lucent vacuoles (asterisks) in the granular layer: remnants of lamellar structures (arrowhead) are visible at the periphery of a vacuole. The intercellular space at the interface between the granular layer and the stratum corneum appear focally and irregularly enlarged, in particular at places of keratinosome fusion with the apical cell surface (arrows, bar = 500 nm). b The intercellular spaces of the lower stratum corneum appear also focally widened and partly filled with a laminated or amorphous material (asterisk). Unusual plasma membrane invaginations containing parallel stacks of lamellae are also visible (arrowhead). Numerous vacuoles, which appear empty or filled with lamellar structures reminiscent of keratinosomes (arrow) and/or an amorphous material, are present within the cytoplasm of horny cells (bar = 200 nm). Sequence analysis of the ALDH3A2 gene, exon 5 of patient 1 and exon 7 of patient 2. c Wild-type sequence of exon 5. d Heterozygous mutation (present in both parents), showing the insertion of an adenine, the mutation is visible as a scrambling of the chromatogram (beginning from black arrow). e Homozygous insertion of an adenine into a stretch of three adenines (red arrow). This mutation leads to a frame-shift with a premature stop codon, TAA, underlined in red. f Wild-type sequence of exon 7. g Heterozygous mutation that results in C to T transversion (black arrow), determining the aminoacid substitution S365L in patient 2