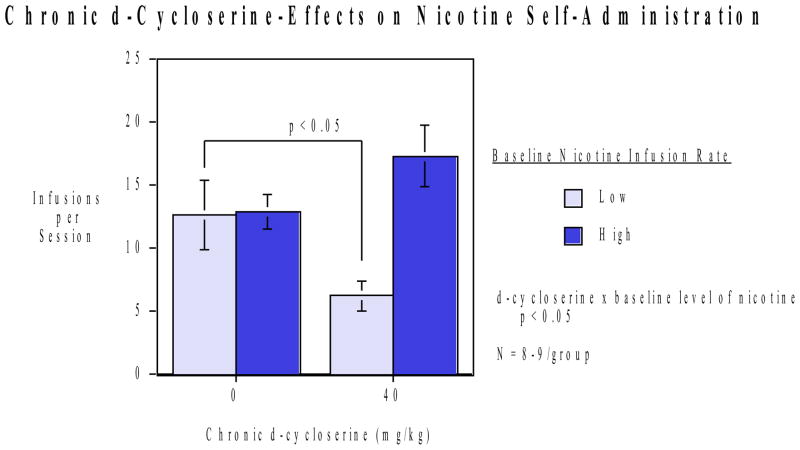
Figure 2.
Repeated d-cycloserine injections and nicotine self-administration (mean±sem). There was a significant (p<0.05) interaction of d-cycloserine x baseline nicotine self-administration level (N=14 controls, N=16 D-cycloserine-treated). In the low-level nicotine self-administration group, chronic d-cycloserine treatment significantly (p<0.05) reduced nicotine self-administration relative to the rats with the same baseline level of nicotine self-administration that were treated with the saline vehicle. In contrast, rats with higher than median levels of baseline nicotine self-administration did not decrease nicotine self-administration relative to controls with high pretreatment nicotine self-administration but rather showed trend toward increased nicotine self-adminsitration.