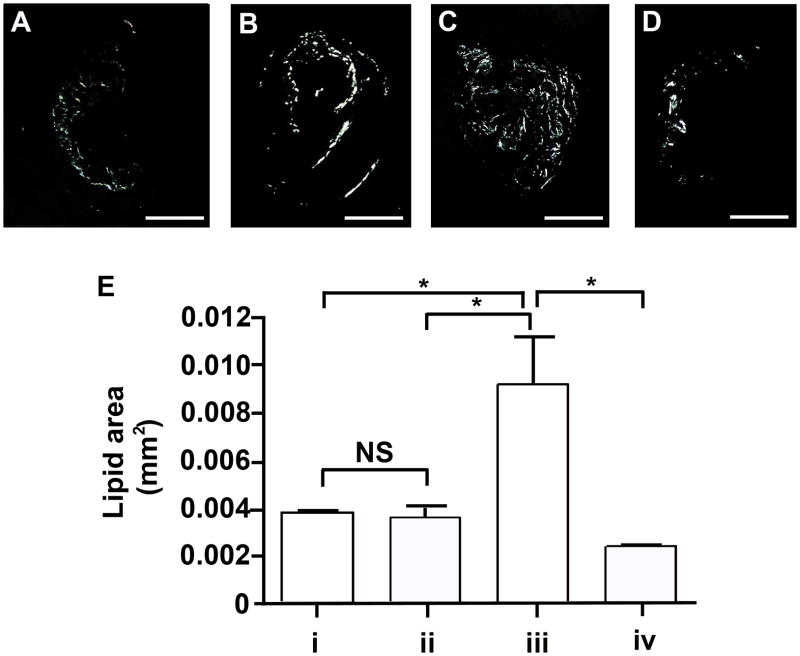
Figure 3. Lipid accumulation in the innominate arteries following P. gingivalis infection.
Representative images of birefringence in plaque corresponding to lipids (total cholesterol esters and cholesterol monohydrate crystals) are shown. (A) group i: uninfected / non-immunized, (B) group ii: uninfected / immunized, (C) group iii: P. gingivalis infected / non-immunized, and (D) group iv: P. gingivalis infected / immunized ApoE−/− mouse. Bar represents 200 μm. (E) Lipid area. In non-immunized ApoE−/− mice P. gingivalis infection increased lipid area compared to uninfected ApoE−/− mice. In P. gingivalis infected ApoE−/− mice, the lipid area was significantly decreased in the immunized group compared to non-immunized group. *p < 0.01, One-way ANOVA. NS indicates no significant difference.