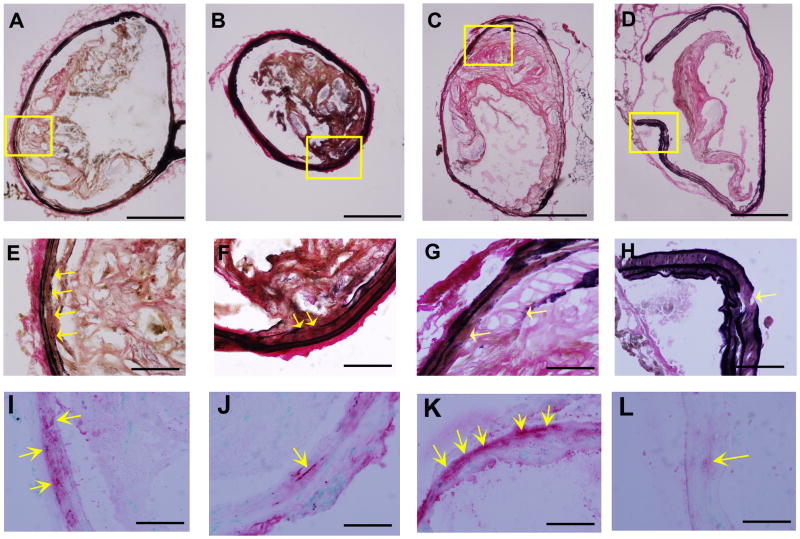
Figure 6. Characterization of elastic laminae in the innominate arteries of P. gingivalis infected mice.
Representative Verhoeff-van Gieson staining for elastin shows elastic laminae (A–H) and α-actin staining for smooth muscle cells (arrows in I–L) in the innominate artery are shown. Discontinuities in the elastic lamina were observed (arrows in E–H). α-actin was detected at the sites of elastin degradation (E–L). (A, E, and I) group i: uninfected / non-immunized, (B, F, and J) group ii: uninfected / immunized, (C, G, and K) group iii: P. gingivalis infected / non-immunized, and (D, H, and L) group iv: P. gingivalis infected / immunized ApoE−/− mouse. Bar represents 200 μm (A–D) and 50 μm (E–L). E and I, F and J, G and K, H and L are the higher magnification of the framed area in A, B, C, and D, respectively.