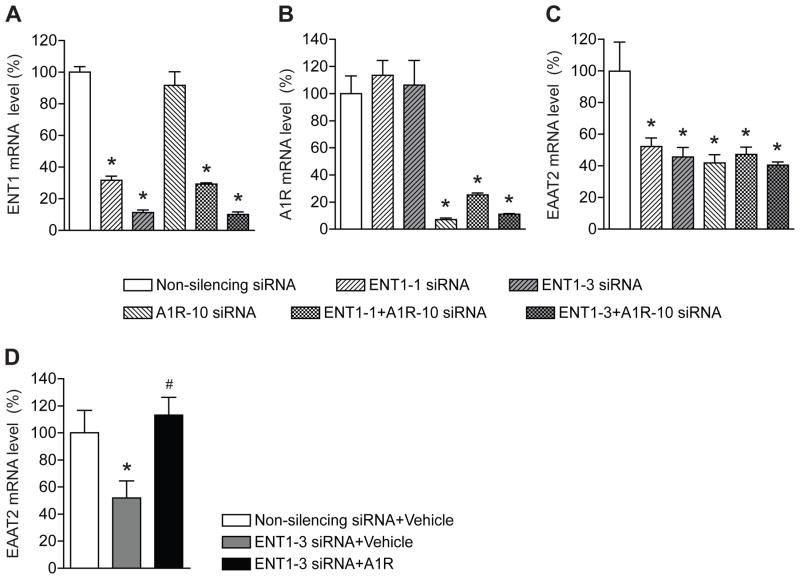
Fig. 2.
Both ENT1 and A1 receptor knockdown decrease EAAT2 expression. (A) ENT1 mRNA levels were specifically knocked down after ENT1 siRNA transfection for 48 h (n = 4). (B) A1R mRNA levels were specifically knocked down after A1R siRNA transfection for 48 h (n = 4). (C) EAAT2 mRNA levels were reduced by co-treatment of ENT1 knockdown and A1R knockdown. 10 nM non-silencing siRNA, ENT1 siRNAs (ENT1-1 and ENT1-3), and/or A1R-10 siRNA were treated together or separately in astrocytes for 48 h. (D) ENT1 siRNA-mediated downregulation of EAAT2 mRNA expression was rescued by A1R overexpression (n = 3~4). The levels of ENT1, A1R, and EAAT2 mRNA were determined by real time RT-PCR using GAPDH as an internal normalization control. n =4; *p < 0.05 compared to non-silencing siRNA-treated cells by unpaired two tailed t-test. All data were expressed as mean ± SEM.