Figure 4.
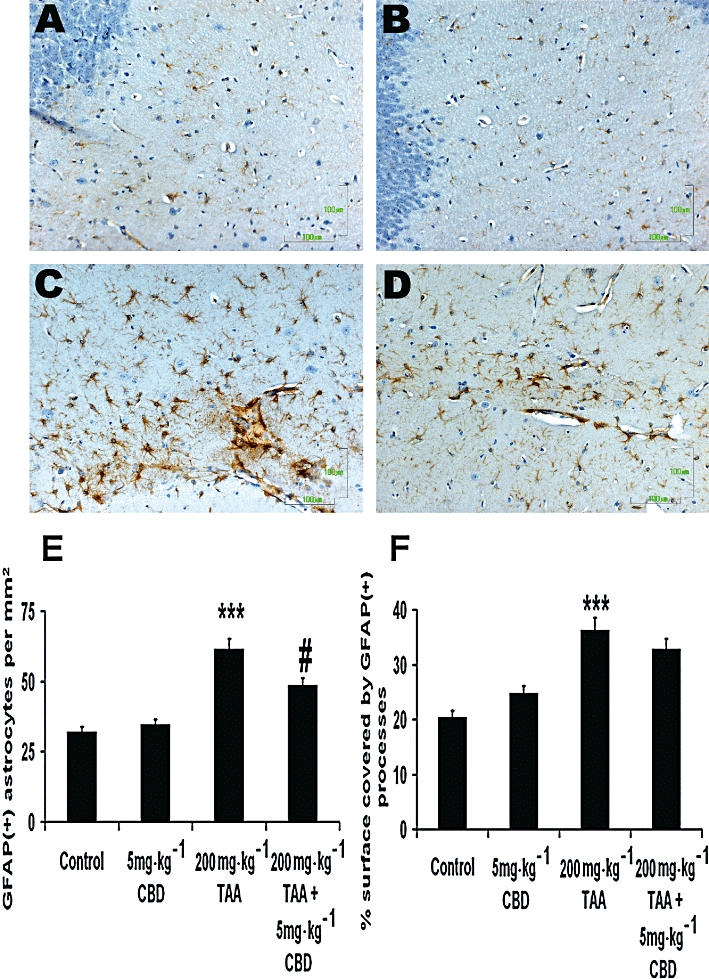
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunohistochemistry indicating the astrocytic reaction throughout the parahippocampal area in naïve controls (A, B) and thioacetamide (TAA)-treated animals (C,D) following treatment with vehicle (A,C) or cannabidiol (CBD) (B,D). CBD treatment had no effect on the astrocytic activation of naïve animals. However, in the case of animals with hepatic encephalopathy, CBD treatment induced significant reduction in the total number of activated astrocytes, although the level of individual cell activation was not impaired. E. Quantification of GFAP-positive cells·mm−2; the number was reduced in TAA mice treated with 5 mg·kg−1 CBD compared to TAA mice treated with vehicle. ***P < 0.001 versus control, #P < 0.01 versus TAA. F. Quantification of GFAP-positive surface in µm2; 5 mg·kg−1 CBD had no effect on the GFAP-positive surface in the brains of TAA-treated mice. ***P < 0.001 versus control. Scale bars: 100 µm.
