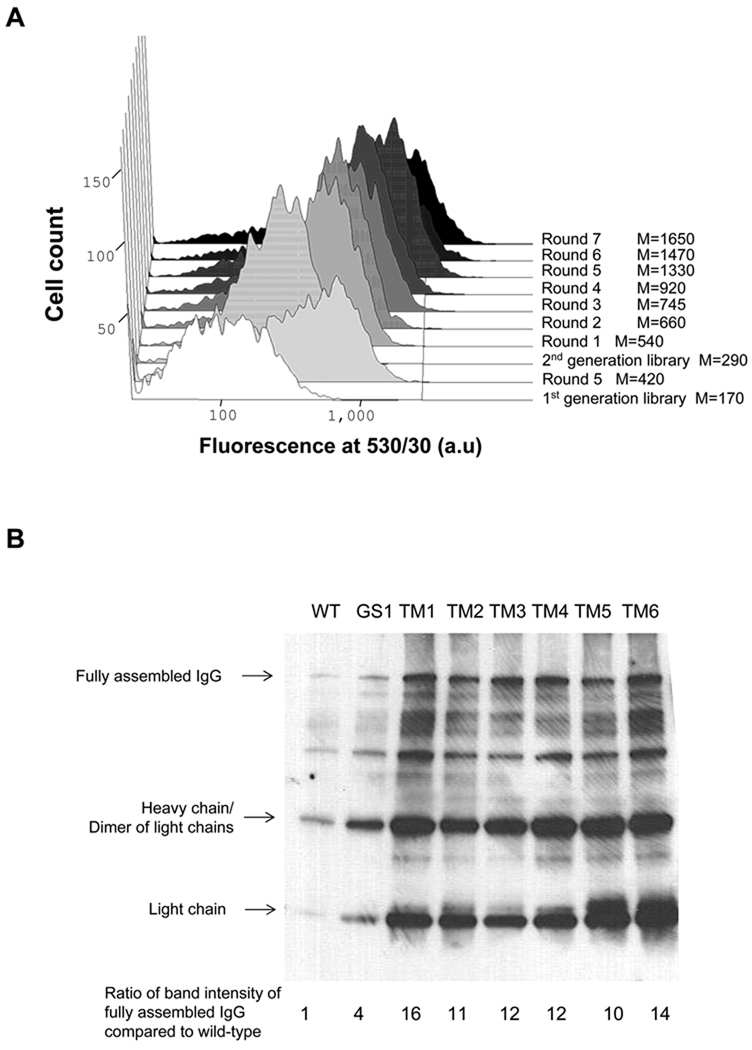
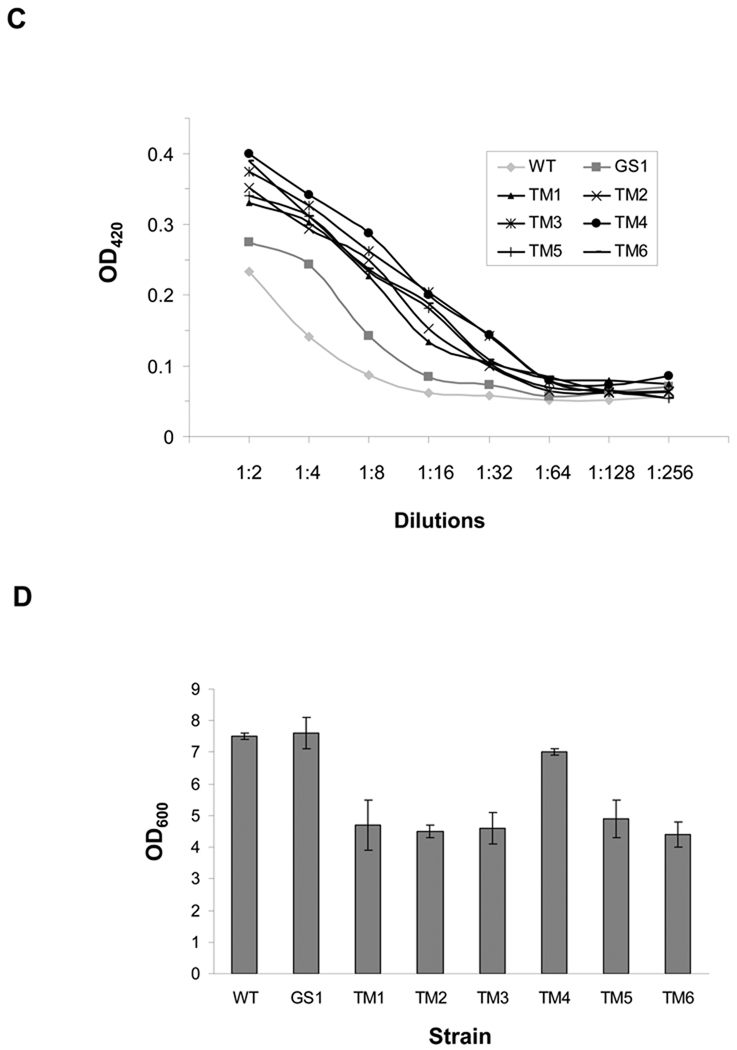
Figure 2. Screening of Chemically Mutated E. coli for IgG Expression.
(A) FACS screening of mutated JUDE-1 cells expressing 26.10 IgG labeled with digoxigenin-BODIPY. M: mean fluorescence intensity. (B) Western blotting of 26.10 IgG expressed in isolated clones after two rounds of mutagenesis and screening. The increase in the yield of fully assembled IgG relative to wild-type (WT) JUDE-1 (lower panel) was determined by scanning densitometry. (C) ELISA assays of IgG level in cell lysates. OD420: optical density at 420 nm. (D) Growth of isolated mutant clones after 16 h of 26.10-IgG overexpression. Experiments were carried out in triplicate and the error bars correspond to one standard deviation from the mean values. In (B) and (C) protein samples were normalized by OD600 so as to contain total protein that corresponds to the same number of bacterial cells. OD600: optical density at 600 nm.