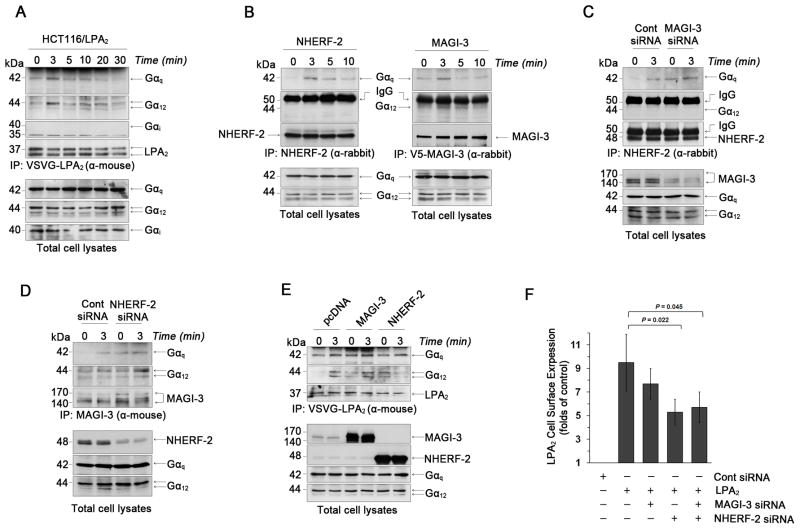
Figure 4. NHERF-2 binds Gαq and stabilizes LPA2 surface expression.
(A) The association of Gα subtypes with LPA2 in HCT116/LPA2 cells treated with 1μM LPA up to 30 min was determined. Expression of Gα subtypes in total cell lysates is shown in the bottom panels. Representative figures from 3 independent experiments are shown. α-mouse; mouse monoclonal antibody. α-rabbit; rabbit polyclonal antibody. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation of Gαq or Gα12 with NHERF-2 (left panel) or V5-MAGI-3 (right panel) was determined in HCT116/LPA2 cells overexpressing NHERF-2 or V5-MAGI-3. The presence of NHERF-2 or MAGI-3, Gαq, and Gα12 in total cell lysates is shown in the bottom panels. (C) The association of Gαq or Gα12 with NHERF-2 was determined in HCT116/LPA2 cells transfected with control siRNA or MAGI-3 siRNA. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation of Gαq or Gα12 with MAGI-3 was examined in HCT116/LPA2 cells transfected with control siRNA or NHERF-2 siRNA. (E) Co-immunorpecipitation of Gαq or Gα12 with LPA2 in HCT116/LPA2 cells transfected with MAGI-3 or NHERF-2 was determined. (F) Surface expression levels of LPA2 were determined by a luminometer-based assay. n ≥ 3 for each experimental set.