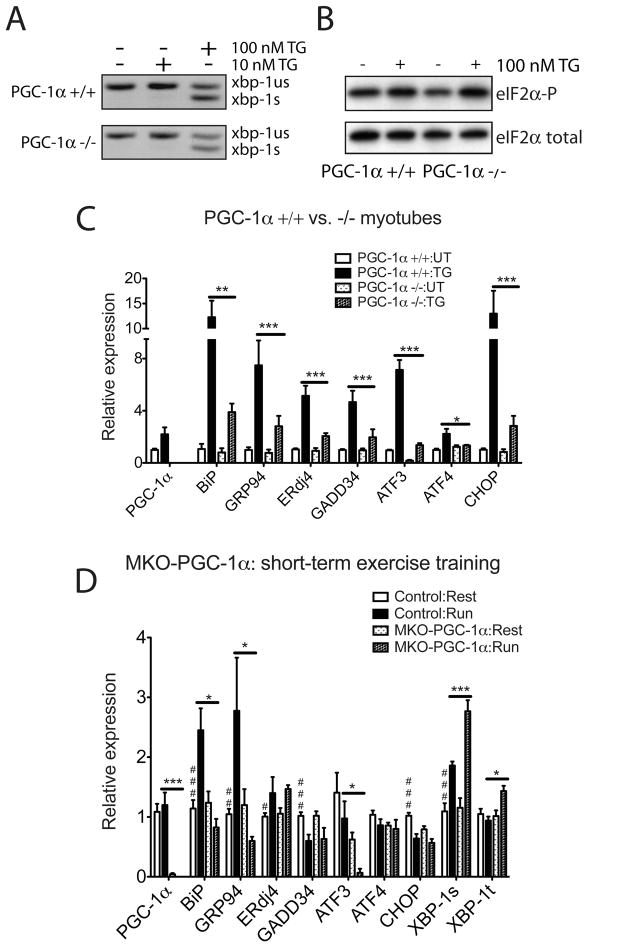
Figure 3. PGC-1α is necessary to upregulate UPR markers expression in primary myotubes upon ER stress and in skeletal muscle after exercise.
(A, B). PGC-1α-deficient myotubes respond to ER stress. A. Total RNA was isolated from wildtype and PGC-1α−/− primary myotubes treated with 10 or 100nM TG for 8hrs. RT-PCR was used to simultaneously detect both spliced (s) and unspliced (us) Xbp1 mRNA. The image is presented in black and white inverted form for greater visual clarity. B. Wild-type and PGC-1α−/− primary myotubes were treated with 100nM TG for 1hr, followed by cell lysis and immunoblot using antibody that detects phosphorylated form of eIF2α and total eIF2α as a loading control. C. PGC-1α−/− primary myotubes are defective in UPR markers upregulation upon ER stress. Total RNA from wildtype and PGC-1α−/− primary myotubes treated with 100nM TG for 16hrs was assayed by realtime RT-PCR for UPR markers expression, normalizing against tbp expression. Data represent means±SD from biological triplicates. *** indicates p <0.005 +/+:TG vs. −/−:TG, **, p <0.01, *, p <0.05. D. MKO-PGC-1α mice are defective in upregulating ER chaperones and experience exacerbated ER stress after repetitive exercise challenges. Total RNA from quadriceps of MKO-PGC-1α and wildtype control mice either sedentary or after four bouts equal distance treadmill running (once a day for 4 days, recover for one day after the last run) was isolated and analyzed by realtime RT-PCR; N=7–8 animals per group. *** indicates p <0.005 MKO-PGC-1α : Run vs. Control : Run; *, p <0.05. ### indicates p <0.005, control : rest vs. control : run, ##, p <0.01, #, p <0.05.