Fig. 4. SLRs (p62/sequestasome-like receptors) capture microbes or associated host structures for delivery to nascent autophagic organelles.
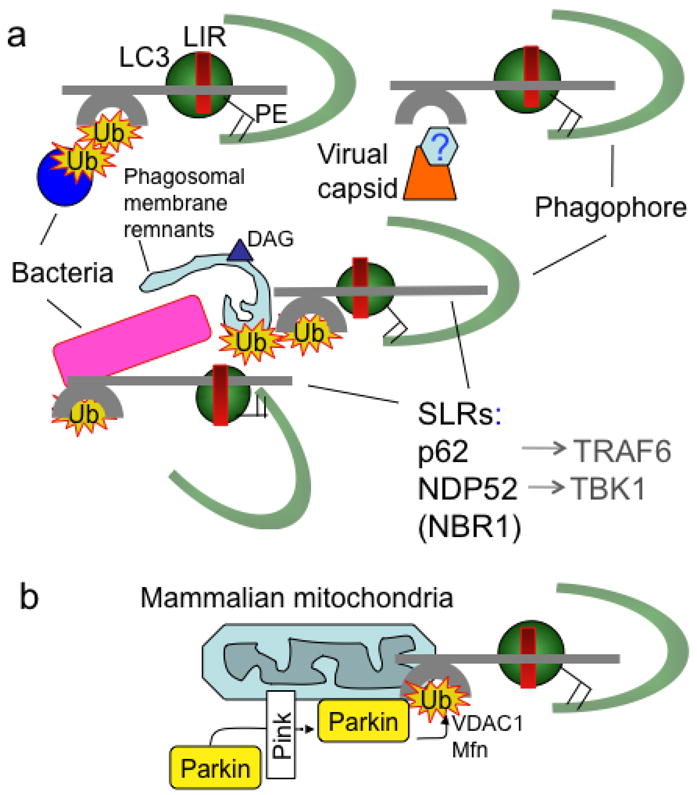
(A). Capture of microbes (bacteria, viral components/capsid) or parasitophorous vacuole membrane remnants by SLRs for autophagic degradation. (B). Capture of terminally depolarized/stressed/damaged mitochondria by SLRs for autophagic removal (“mitophagy”). SLRs include p62 sequestasome, NDP52, NBR1. All of these molecules serve as autophagic adapters by the virtue of interacting with LC3 (one of mammalian Atg8s) or other mammalian Atg8 paralogs, often through a motif termed LIR (LC3 interaction region, with a variation of the ‘WXXL’ motif: D/EW/FE/DXLI/V). SLRs also interact with proinflammatory signaling factors such as TRAF6 and TBK1. Ub, ubiquitin tags recognized by ubiquitin binding regions (e.g. UBA in p62 and NBR1 or zinc finger in NDP52). DAG (triangle), diacylglicerol, a lipid tag found on microbe-harboring phagosomal membranes as a signal for autophagic degradation that may act independently of ubiquitin tags (Ub). Hexagon labeled ‘?’, tags associated with viral capsids have not been identified. Green semicircle, phagophore. PE, phosphatidylethanolamine. Parking, ubiquitin E3 ligase recruited to stressed mitochondria by Pink, with ubiquitination of VDAC1 (a component of mitochondrial permeability transition pore and the most abundant mitochondrial outer membrane protein) and Mfn (mitofusin, a GTPase that controls mitochondrial dynamics and fusion). Note the striking similarity between removal of intracellular microbes (a) and mitochondria (b) by SLRs, possibly reflecting ancient evolutionary relationships since mitochondria evolved from α-proteobacterial (Rickettsia-like microorganisms) symbionts.
