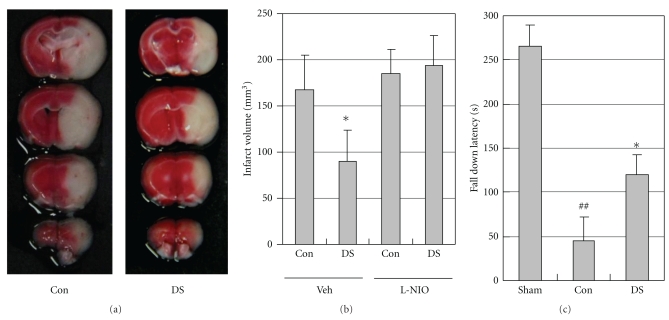
Figure 4.
DS reduces cerebral ischemic injury. (a) Representative photographs of coronal brain sections stained with 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride in saline- (Con, left)—and DS-treated mice (right). Mice were orally administered saline or 600 mg/kg DS twice per day for 3 days before the ischemic insult. Mice were subjected to 90 min of MCAO followed by 22.5 h of reperfusion. White indicates the infarct area. (b) Effect of DS on infarct volume in saline- and L-NIO-treated mice at 24 h after ischemia. Infarction volume was calculated by an indirect measurement. DS significantly reduced cerebral infarct size; however, it did not affect brain infarction in L-NIO-treated mice. (c) Effect of DS on ischemia and reperfusion induced impairment of motor coordination. DS markedly prevented ischemia-reperfusion induced motor incoordination. Data are expressed as means ± SEM of six separate experiments. *P < .05 versus control; ## P < .01 versus Sham group.