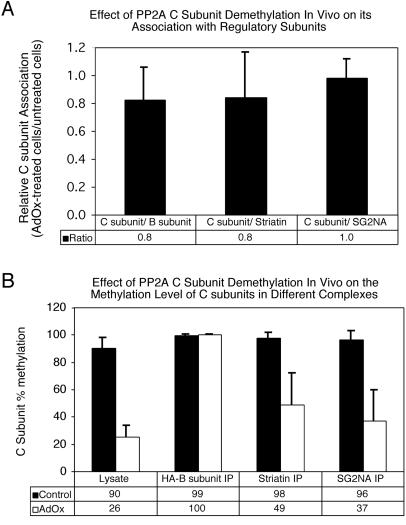
Figure 7.
Effect of PP2A C subunit demethylation in vivo on PP2A complexes. NIH3T3 cells stably expressing HA-tagged Bα subunit were treated sequentially with 100 nM okadaic acid for 14 h followed by 200 μM AdOx for 30 h to reduce C subunit methylation. Cell lysates were prepared from treated (AdOx) and untreated (Control) cells and immunoprecipitations were performed using HA-tag (12CA5), striatin, and SG2NA antibodies. Immunoprecipitates (IP) and lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and probed with HA-tag, striatin, SG2NA, and methylation-sensitive and methylation-insensitive C subunit antibodies using enhanced chemiluminescence. A Bio-Rad Fluor S-Max chemilumimager was then used to calculate 1) the ratio of total C subunit (methylation-insensitive antibody) to regulatory subunit in each immune complex and 2) the methylation level of C subunit in the lysates and immune complexes. (A) Effect of PP2A C subunit demethylation on regulatory subunit association. C subunit association (C subunit/regulatory subunit) was calculated for each regulatory subunit for both control and treated cells. The ratio of C subunit association in treated cells to C subunit association in untreated cells is shown for each regulatory subunit. (B) Effect of PP2A C subunit demethylation on the methylation level of C subunits bound to different regulatory subunits. Shown is the percentage of methylation of C subunit in cell lysates and immunoprecipitations prepared from control and treated cells. The data shown represent the average and SD of at least three independent experiments. The error bars on C subunits associated with Bα are very small because the C subunit in these complexes was essentially 100% methylated in each experiment.