FIGURE 1.
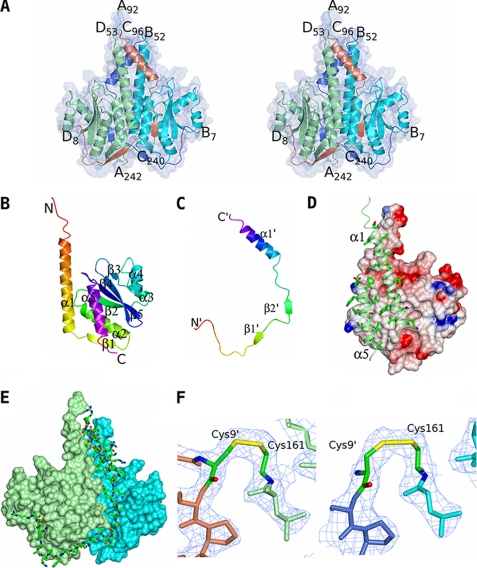
The crystal structure of CSpoIISA·SpoIISB. A, the structure of the toxin-antitoxin heterotetramer is shown in ribbon representation and colored by chain with a transparent molecular surface overlaid. The CSpoIISA chains are in light green and cyan, and the SpoIISB chains are colored light blue and coral. The N and C termini of the chains are labeled. B and C, ribbon tracings of the CSpoIISA and SpoIISB chains respectively colored ramped from their N termini (red) to their C termini (magenta). The secondary structure elements and the N and C termini are labeled with those of SpoIISB distinguished by apostrophes. D, the CSpoIISA dimer interface. CSpoIISA chain C is shown as an electrostatic surface with regions of positive and negative charge colored blue and red, respectively, and with apolar surfaces in white/gray. For clarity the CSpoIISA chain A has been truncated so that only the dimer-forming helices α1 and α5 are shown. These are shown as light green ribbons with side chains proximal to the dimer interface shown. The abundance of apolar interactions across the dimer interface is apparent. E, the interactions between SpoIISB and the CSpoIISA dimer. The CSpoIISA chains A and C are shown as surface representations and colored in light green and cyan, respectively. SpoIISB chain B is shown in cylinder representation and colored by atom type (carbon, green; nitrogen, blue; oxygen, red; sulfur, yellow). Its extensive contacts with both CSpoIISA chains are apparent. F, electron density in the vicinity of the disulfide bonds between Cys161 of CSpoIISA and Cys9′ of SpoIISB in the AD (left) and BC heterodimers (right). The chains are colored as in A, with the cysteines colored by atom type. The 2Fobs − Fcalc map is contoured at the 1σ level. These images and those in Fig. 3 were produced using the molecular graphics program CCP4MG (48).