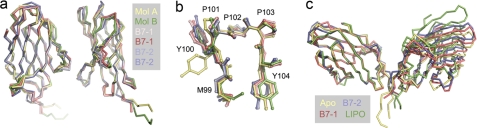
FIGURE 5.
The rigid-body interaction of CTLA-4 with its ligands. In a the two halves of the apo homodimer, i.e. mol A (yellow) and mol B (green), are superimposed using Coot with two copies of the CTLA-4 monomer seen in the crystals of the CTLA-4/B7-1 complex (red, light red; Ref. 10) and in the crystals of the CTLA-4·B7-2 complex (blue, light blue; Ref. 9). The only regions of significant variation are in the positions of the BC and CC′ loops, the C″ strand and its adjacent loops, with the largest differences being those between mol A and mol B of the apo structure. Structures are shown as α-carbon representations. In b the structures of the 99MYPPPY104 FG loops of the apo and complex structures, shown in ball-and-stick format, are compared following superposition of the loops with Coot. The color scheme is the same as that used in a; the largest differences are observed for the two apo structures. In c, the structure of the apo-CTLA-4 homodimer (yellow) is compared with that of the homodimer from the B7-1 (red), B7-2 (blue), and lipocalin (green; Ref. 51) complexes, all shown as α-carbon representations following superposition on mol A of apo-CTLA-4.