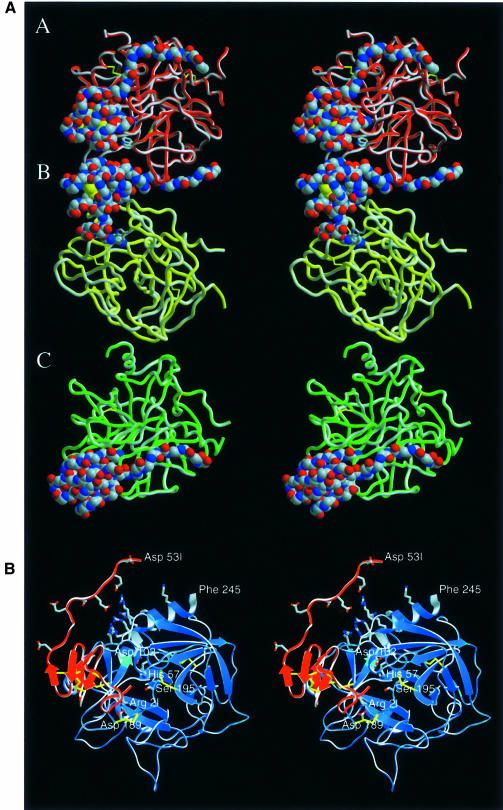
Fig. 1. Crystal structure of the human thrombin–haemadin complex. (A) Structure of the crystallographic trimer present in the asymmetric unit. Monomers are labelled A, B and C. Thrombin molecules are shown as red, yellow and green ribbons; the Cα traces of the three inhibitors are presented as colour-coded van der Waals spheres (red, oxygen; blue, nitrogen; grey, carbon). (B) Stereo diagram of complex molecule A. The protease is shown in its ‘standard orientation’ (Bode et al., 1992), i.e. with the active-site cleft facing the viewer and substrates running from left to right. Side chains of the catalytic triad residues are shown explicitly, as well as the side chains of the interacting residues Asp189 (thrombin) and Arg2I (haemadin) (colour coded as in Figure 1A). Also shown (unlabelled) are the side chains of the basic residues of the heparin-binding site (thrombin), as well as the side chains of the acidic residues of haemadin’s C-terminal tail. This figure and Figures 3, 5A, 7A and 8 were prepared with SETOR (Evans, 1993).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.