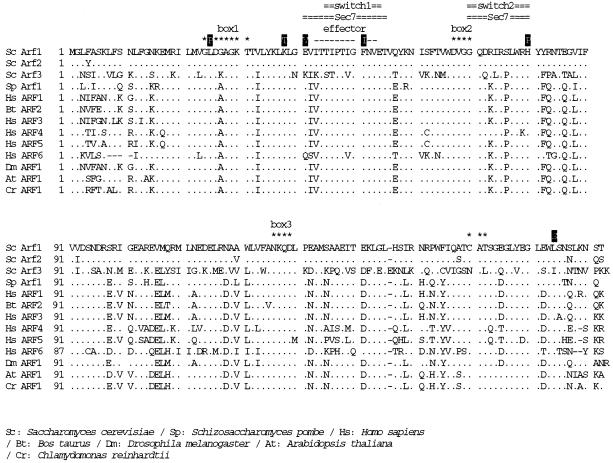
Figure 1.
The mutation points of yeast Arf1p, which cause ts phenotype as a single mutation, and the sequence comparison of Arf1p from various organisms. Dots indicate identity with S. cerevisiae Arf1p. Consensus GTP-binding (DVGG, NKQD, and CAT) and hydrolysis (GX4GK) sequences are marked with asterisks. The putative effector domain is shown by dashes. The site of Sec7 domain interaction on human ARF1 and the switch 1 and switch 2 GTPase regions (Mossessova et al., 1998) are marked with double lines. Sc, S. cerevisiae; Sp, Schizoaccharomyces pombe; Hs, Homo sapiens; Bt, Bos taurus; Dm, Drosophila melanogaster; At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Cr, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The database accession numbers from GenBank are as follows: Sc Arf1, P11076; Sc Arf2, P19146; Sc Arf3, P40994; Sp Arf1, AL031534.1; Hs ARF1, NM 001658.1; Bt ARF2, P16500; Hs ARF3, NM 001659.1; Hs ARF4, NM 001660.1; Hs ARF5, NM 001662.1; Hs ARF6, NM 001663.1; Dm ARF1, P35676; At ARF1, P36397; Cr ARF1, U27120.1.