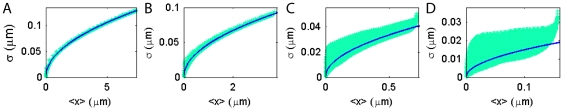
Figure 9. Fluctuation versus mean extension of internal segments of the strongly confined DNA in 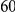 nm channels (Eq.13 and Eq.14).
nm channels (Eq.13 and Eq.14).
The contour lengths of the DNA are (A) 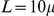 m, (B)
m, (B) 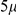 m, (C)
m, (C) 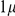 m and (D)
m and (D) 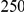 nm. For a long DNA (A and B), data from internal segments of various locations of the chain collapse on the a curve with
nm. For a long DNA (A and B), data from internal segments of various locations of the chain collapse on the a curve with 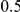 power law (light green). The result agrees with Eq.9 (blue), which is derived for the end-to-end fluctuation of a confined DNA. For short DNA however (C and D), no power law is found as data from various locations of the chain do not collapse onto a single curve (light green). Therefore, formulae derived for the end-to-end fluctuation of the confined DNA, such as Eq.9 (blue), cannot be used for internal fluctuation. The boundary effect is so significant that the rms fluctuation
power law (light green). The result agrees with Eq.9 (blue), which is derived for the end-to-end fluctuation of a confined DNA. For short DNA however (C and D), no power law is found as data from various locations of the chain do not collapse onto a single curve (light green). Therefore, formulae derived for the end-to-end fluctuation of the confined DNA, such as Eq.9 (blue), cannot be used for internal fluctuation. The boundary effect is so significant that the rms fluctuation  not only depends on
not only depends on 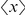 , but also on the location of the internal segments.
, but also on the location of the internal segments.