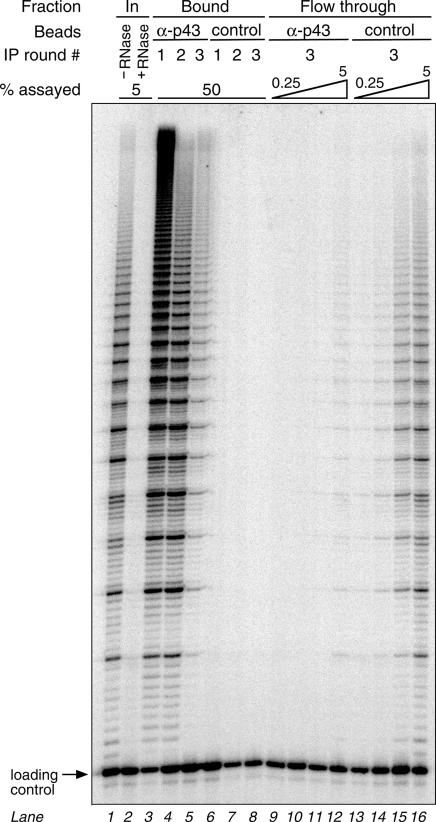
Fig. 7. The vast majority of telomerase activity is associated with p43. Euplotes aediculatus nuclear extract was partially purified by glycerol gradient centrifugation and subjected to three consecutive rounds of immunodepletion with α-p43 antibody beads or control antibody beads, as described in the legend to Figure 6. Input, bound and flowthrough fractions were assayed for telomerase activity by measuring extension of a telomeric primer in the presence of a radiolabeled substrate nucleotide, followed by phenol/chloroform extraction and separation of telomerase products in a denaturing polyacrylamide gel. Five percent of input nuclear extract before (lane 1) or after (lane 2) RNase A treatment, 50% of α-p43 antibody beads (lanes 3–5) or control antibody beads (lanes 6–8), as well as 0.25, 0.5, 2.5 and 5% of the final flowthroughs from the α-p43 antibody beads (lanes 9–12) or control antibody beads (lanes 13–16) were assayed. Equal amounts of an end-labeled 23mer oligonucleotide were added to the samples prior to phenol/chloroform extraction to control for recovery and loading.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.