Figure 1.
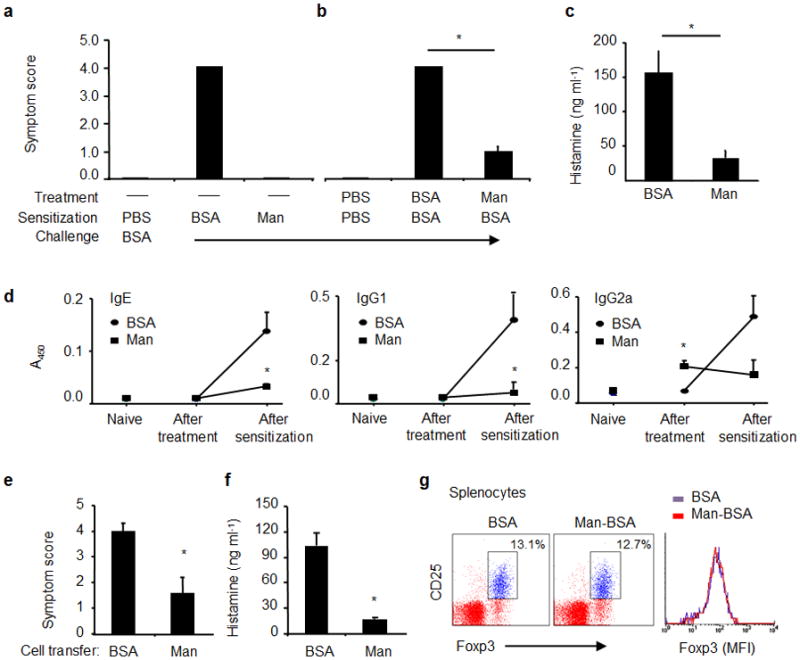
Antigen-induced anaphylaxis in C3H/Hej mice. (a) Mice were sensitized with PBS, BSA (200 μg/mouse) or Man51-BSA (Man, 200 μg/mouse) with CTX (10 μg/mouse) and challenged with BSA (1 mg/mouse). The severity of anaphylactic responses was scored 30 min after antigen challenge by the scoring system24- from 0, no sign of shock to 5, death. (b) Man51-BSA suppressed BSA-induced anaphylaxis. Mice were pretreated daily on three consecutive days with BSA or Man51-BSA (Man) at 200 μg/mouse, followed by oral sensitization and challenge with BSA. *p < 0.05. (c) The levels of plasma histamine in the same groups of mice as in (b). (d) The relative levels of specific IgE, IgG1 and IgG2a Abs in naïve mice and those after the treatment (before BSA sensitization) with BSA or Man51-BSA, or those after BSA sensitization. *p < 0.05 vs BSA. 8–14 mice per group. Adoptive transfer of splenocytes suppressed BSA-induced anaphylaxis. (e) Symptom scores and (f) plasma histamine levels in sensitized and challenged mice receiving spleen cell transfer from BSA- or Man51-BSA (Man)-treated mice. *p < 0.05. 6–8 mice per group. (g) Representative flow analysis of splenic Foxp3+ Tregs in BSA- or Man51-BSA (Man-BSA)-treated mice. The % of CD25+Foxp3+ cells gated on CD4+ cells and the relative intensity (MFI) of Foxp3 are shown. 3–5 mice per group. Results are representative of 2 independent experiments.
