Figure 5.
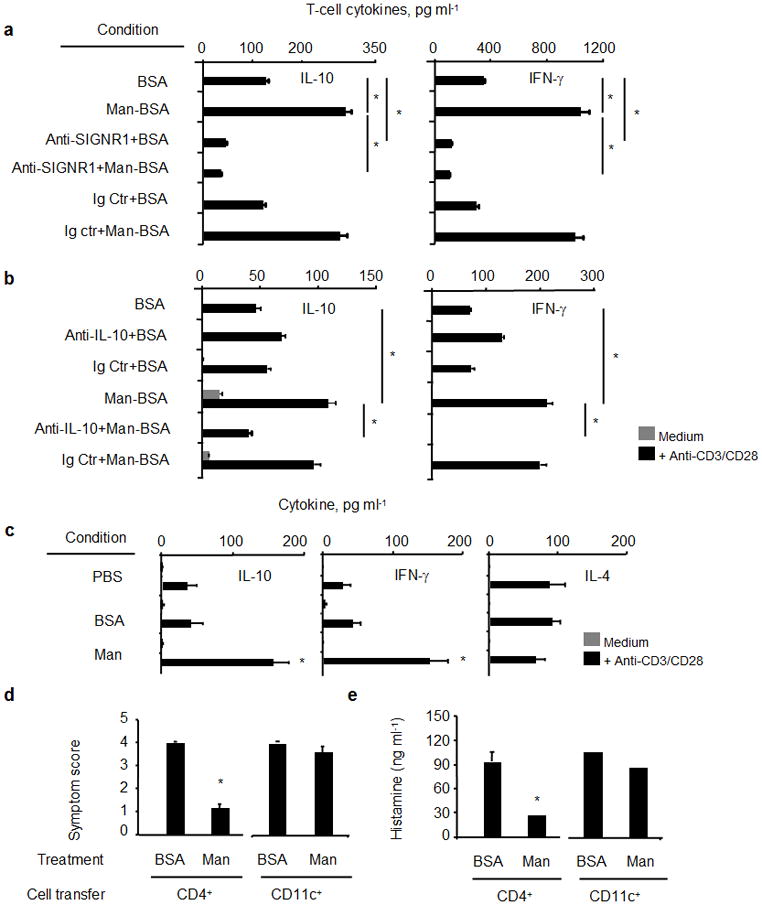
Increased IL-10- and IFN-γ expression in T cells in vitro when co-cultured with Man51-BSA (Man) pulsed LPDCs (CD11c+), in the presence or absence of (a) SIGNR1-specific or isotype control (Ig Ctr) antibodies, (b) neutralizing IL-10-specific (5 μg/ml) or isotype control (Ig Ctr) antibodies. T-cell cytokines, IL-10 and IFN-γ, were measured by ELISA. (c) Increased IL-10-and IFN-γ-expressing T cells from mice receiving oral administration of PBS, BSA or Man51-BSA (Man, 200 μg/mouse). *p < 0.05 vs PBS or BSA. Adoptive transfer of splenic CD4+ T cells suppressed BSA-induced anaphylaxis. (d) Symptom scores and (e) plasma histamine levels in sensitized and challenged mice receiving transfers of CD4+ T cells or CD11c+ DCs from BSA- or Man51-BSA (Man)-treated mice. *p < 0.05. 6–8 mice per group.
