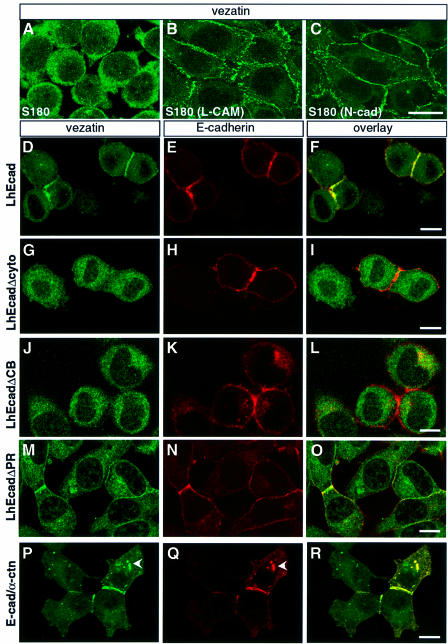
Fig. 5. Vezatin interacts with the cadherin–catenin complex. (A–C) Localization of vezatin in S180 cells expressing chicken E-cadherin (L-CAM) or N-cadherin (N-cad). In S180 fibroblasts (A), which lack E-cadherin and adherens-like junctions, vezatin is distributed throughout the cytoplasm. In contrast, in stably transfected S180 cells expressing chicken L-CAM (B) or N-cadherin (C) an intense vezatin labelling is detected at cell–cell contacts. (D–R) Vezatin localization in transfected L2071 cells expressing different truncated E-cadherin (D–O) or E-cadherin–α-catenin chimeras (P–R). In L cells stably transfected with the entire human E-cadherin (L-hEcad), vezatin (D) as well as E-cadherin (E) is recruited to the cell–cell contacts (F). In contrast, in L cells stably expressing hEcad lacking either the cytoplasmic domain (L-hEcadΔCyto) (G–I) or the β-catenin binding domain (L-hEcadΔCB) (J–L) vezatin has a cytoplasmic localization. In L cells expressing hEcad lacking the p120-catenin binding site (L-hEcadΔPR) vezatin is recruited to the cell junction (M–O). In L cells expressing the E-cadherin–α-catenin chimera, linking the E-cadherin transmembrane domain directly to the last 398 C-terminal amino acids of α-catenin, vezatin is detected at the cell–cell junctions (P–R). Note the cytoplasmic localizations of vezatin and E-cadherin–α-catenin chimera (arrowheads). Bar, 10 µm.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.