Figure 1.
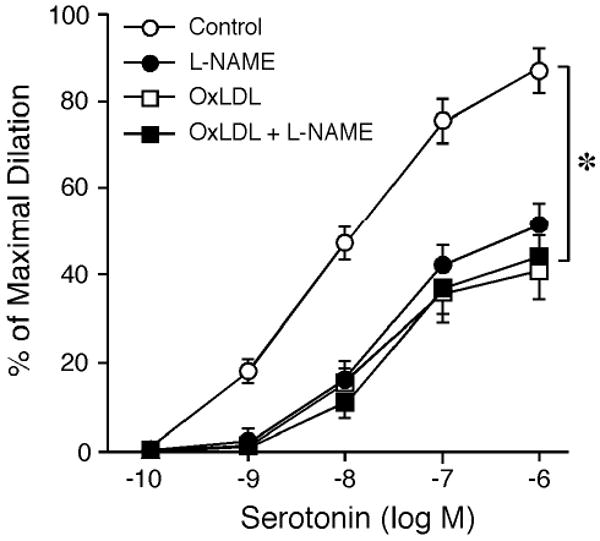
Effect of OxLDL on coronary arteriolar dilation to serotonin. The coronary arterioles dilated in a concentration-dependent manner to serotonin (Control; n=15). The serotonin-induced vasodilation was significantly inhibited by either L-NAME (10 μM; n=5) or OxLDL (0.5 mg protein/ml; n=6). The inhibitory effect of L-NAME was comparable to that of OxLDL. The combination of OxLDL and L-NAME treatment did not further inhibit vasodilation to serotonin (n=4). *P<0.05 vs. Control.
