Figure 6.
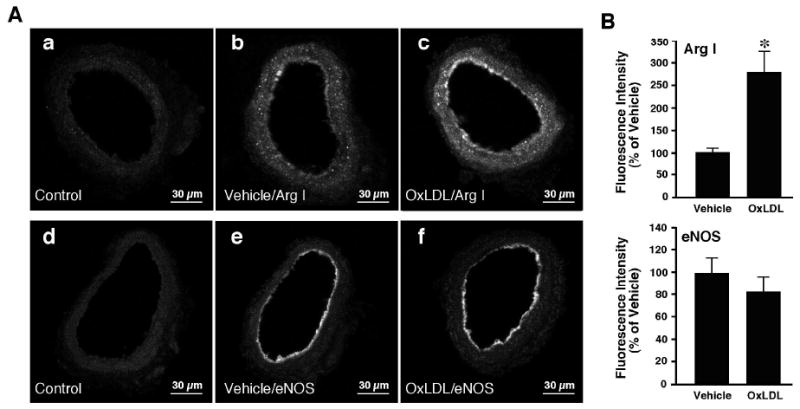
Immunohistochemical detection of arginase I and eNOS in coronary arterioles. A: Cross-sectional view of fluorescein-labeled vessels after treatment with non-immune immunoglobulin, anti-arginase I or anti-eNOS primary antibodies. Panels a and d: Images obtained from vessels treated with non-immune immunoglobulin (Control; n=6). Panels b and e: images obtained from vessels treated with PSS (Vehicle) and immunolabeled with arginase I (Arg I) (panel b; n=6) or eNOS (panel e; n=6) antibody. Panels c and f: Images were obtained from vessels treated with OxLDL (0.5 mg protein/ml) and immunolabeled with arginase I (Arg I) (panel c; n=6) or eNOS (panel f; n=6) antibody. Fluorescence signals for arginase I were detected in both the endothelium and smooth muscle of the vessels (panels b and c). eNOS fluorescence signals were detected in the endothelium only (panels e and f). B: Quantitative analyses of arginase I and eNOS fluorescence signals in vessels treated with vehicle or OxLDL. The arginase I signal intensity was significantly increased in both the endothelial and smooth muscle cells of the vessel treated with OxLDL. OxLDL did not alter eNOS signal intensity.
