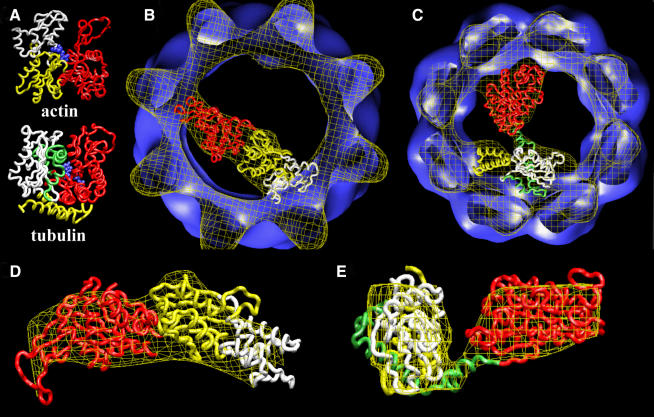
Fig. 4. Docking of the atomic structures of actin and tubulin. (A) Atomic structures of actin (Kabsch et al., 1990) and tubulin (Nogales et al., 1998a). Both proteins are divided into two domains: the N-terminal domain (red domain) and the C-terminal domain (yellow and white domains in actin and yellow, green and white domains in tubulin). The blue region corresponds to the nucleotide (ADP in actin, GTP in tubulin). (B) Docking of the two domains of the atomic structure of actin with the cryo-electron microscopy three-dimensional reconstruction of actin complexed to CCT (Llorca et al., 1999b). The code colours are the same as in (A), with the white domain corresponding to the fragment that permits a chimeric protein to bind strongly to CCT (β-actin.sub4) (Llorca et al., 1999b). (C) Docking of the two domains of the atomic structure of tubulin with the cryo-electron microscopy three-dimensional reconstruction of tubulin complexed to CCT (Figure 2). The code colours are the same as in (A), with the white, green and yellow domains corresponding to the tubulin fragments inserted in the chimeric proteins Ha-Ras–β-tubulin fragments 5, 3 and 4, respectively. (D) Enlarged side view of the docking of actin shown in (B). (E) Enlarged side view of the docking of tubulin shown in (C).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.