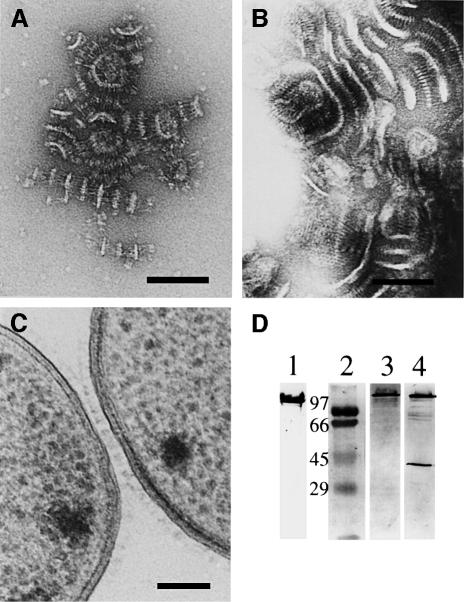
Fig. 6. Visualization of different characteristic features of YadA of strain WA-314. (A) After incubation of small YadA-covered vesicles with Octyl-POE, the oligomers start to aggregate with each other. The head domains interact in a zipper-like fashion, whereas the anchor domain forms membrane-like structures such as vesicles or sheets. (B) Prolonged incubation results in the formation of large, even macroscopically visible aggregates. (C) Electron micrograph of a cross-section of autoagglutinated Yersinia cells. The interaction of the cells is mediated by an interaction of the YadA layers on the cell surfaces. (D) SDS–PAGE (lane 1) and immunoblotting of purified YadA aggregates of WA-314. Lane 1, oligomeric YadA, Coomassie Blue stain; lane 2, molecular weight markers (kilodaltons); lanes 3 and 4, immunoblot showing oligomeric YadA and partially disintegrated YadA, respectively (monomer 41 kDa).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.