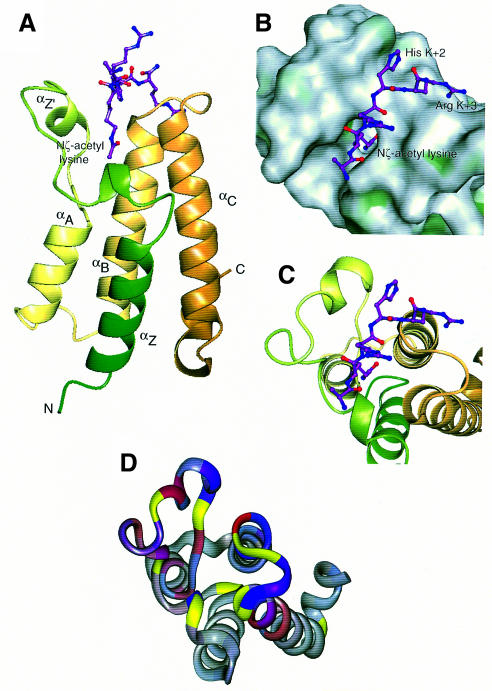
Fig. 4. Overall structure and peptide binding. (A) Ribbon diagram showing the bundle of four main α-helices, Z, A, B and C, with the Nζ-acetyl lysine side chain of the peptide bound in a deep slot at the top of the bundle. The ribbon is coloured from green (N-terminus) to gold (C-terminus). (B) ‘Top’ view of the molecular surface coloured by hydrophobic potential (dark green marks favourable regions for hydrophobic interaction; grey, less favourable; light green, intermediate). The five visible residues of the peptide fit into a shallow groove, with the acetyl lysine side chain in a deep slot. The hydrophobic surface at the base of the pocket formed by Phe352 and Val356, as well as that lining the side of the pocket formed by Pro351, Val 356, Tyr364 and Tyr413, are not easily visible in this view. (C) The same view as (B), showing the underlying helices coloured as in (A). (D) Mapping of backbone NH chemical shift changes onto residues 329–438 of the peptide backbone of the Gcn5p bromodomain in the same orientation as (B) and (C). 1H and 15N changes are indicated in red and blue, respectively. The colours are merged so that the shade reflects the relative contributions of the two shift changes and the intensity reflects the magnitude of the changes. Residues for which no backbone amide groups were assigned are shown in yellow (see text).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.