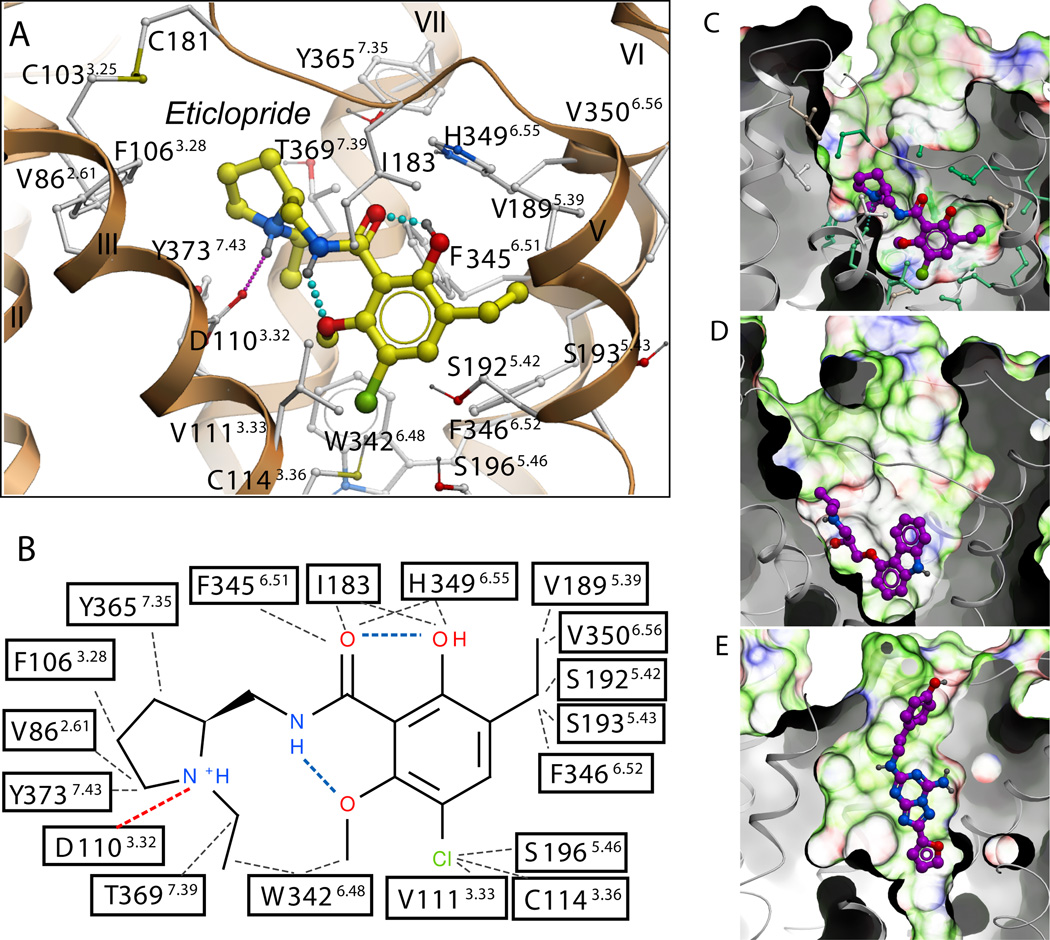
Fig. 3.
Structural diversity of ligand binding sites in GPCR structures. (A) Close up of the eticlopride binding site showing the protein-ligand interaction. (B) Chemical structure of eticlopride and interactions with the D3R residues; hydrophobic contacts are colored in gray dots, hydrogen bonds in blue, and salt bridges in red. The ligand binding sites in (C) D3R, (D) β2AR (PDB ID: 2RH1), and (E) A2AAR (PDB ID: 3EML) crystal structures are shown in exactly the same orientation. A semi-transparent skin shows the molecular surface of the receptor, colored by the residue properties (green-hydrophobic, red-acidic, and blue-basic). Corresponding ligands, (C) eticlopride, (D) carazolol, and (E) ZM241385 are shown with carbon atoms colored magenta. For the D3R pocket, residues conserved between D3R and β2AR are colored turquoise and non-conserved are in gray.