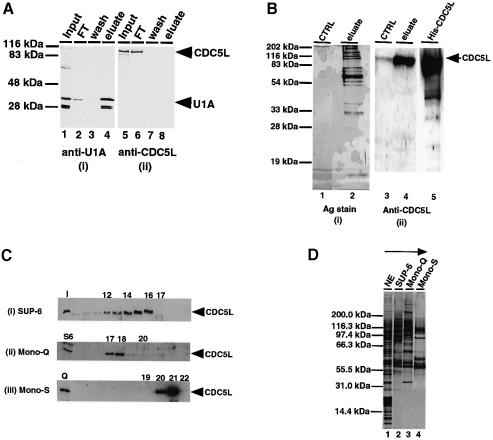
Fig. 4. Purification of a multiprotein complex containing CDC5L. (A) Probing of purified snRNPs for the presence of CDC5L. Total snRNPs in HeLa nuclear extract were purified as described in Materials and methods. About 15–20 µg of purified snRNPs fractions were separated on a 12% SDS–PAGE gel and the fractions probed with anti-U1A and anti-CDC5L antibodies. Lanes 1 and 5 contain the input nuclear extract. Lanes 2 and 6 contain the column flow-through fractions, while lanes 3 and 7 have the column wash fractions. Lanes 4 and 8 contain the column eluate obtained using m3G-cap dinucleotide. The fractions in panel (i) were probed with anti-U1A antibody and the fractions in panel (ii) probed with anti-CDC5L antibody. Arrowheads on the right of the figure indicate the bands representing U1A and CDC5L. (B) Purification of the CDC5L complex by immunoaffinity chromatography. The complex was purified by passing 80–100 mg of HeLa nuclear extract through a column containing covalently coupled anti-CDC5L antibody. The column was eluted using glycine (see Materials and methods) and the eluate separated on a 12% SDS–PAGE gel and the gel either silver stained (i) or western blotted and probed with anti-CDC5L antibody (ii). Lanes 1 and 3 contained the control samples, i.e. eluate from the column pre-blocked with antibody specific peptide. Lanes 2 and 4 contained the eluate from the antibody column and lane 5 contained purified, E.coli expressed, His6-tagged CDC5L. (C) Identification of chromatographic fractions containing CDC5L in the tandem purification procedure. Aliquots of fractions from each purification step were separated on a 4–12% pre-cast SDS–PAGE gel (Novex) and the presence of CDC5L protein confirmed by probing western blots with anti-CDC5L antibody. The numbers at the top of each panel represent the fraction numbers and the arrowheads on the right of each panel indicate the position of CDC5L in the gel. Panel (i) contained fractions from the gel filtration column (Superose-6). The lane marked I contained the input nuclear extract. Panel (ii) shows fractions from the Mono-Q column and panel (iii) contains fractions from the Mono-S column. The lanes marked S6 and Q represent pools of Superose-6 and Mono-Q fractions containing CDC5L that were used as the input for the purification procedure. (D) Tandem chromatographic purification of the CDC5L-associated complex in HeLa nuclear extract. Aliquots of pooled CDC5L-containing fractions from each purification step were separated on a 4–12% pre-cast SDS–PAGE gel (Novex) and the protein bands revealed by silver staining. Lane 1 contained the input nuclear extract. Lanes 2–4 contained pools of the Superose 6, Mono-Q and Mono-S column fractions containing CDC5L, respectively. The arrow at the top of the figure indicates the purification steps of the CDC5L complex from HeLa nuclear extract. The first step involves gel filtration (Superose-6 or SUP-6) and the last step is an ion exchange purification of the complex on a Mono-S column.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.