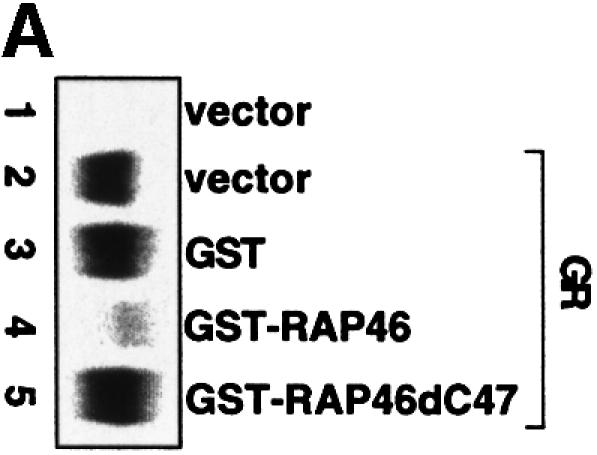
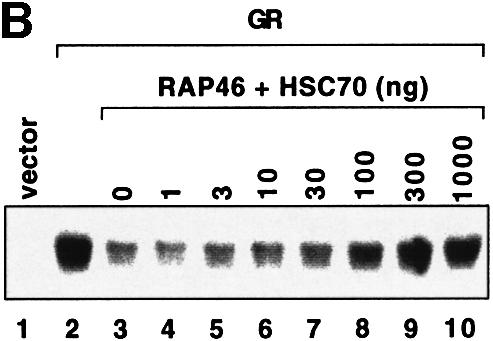
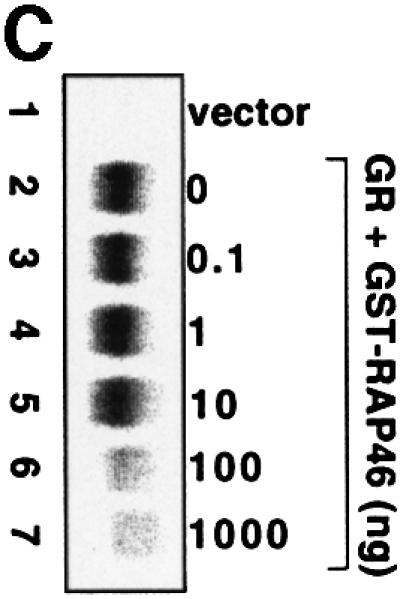
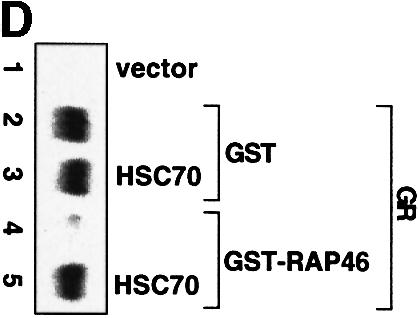
Fig. 4. In vitro cell-free system for studying the effect of RAP46 on DNA binding by the GR. One hundred thousand COS-7 cells in 3.4 cm culture dishes were transiently transfected by the Fugene transfection procedure with 0.9 µg empty expression vector or with an expression vector encoding the GR. Whole-cell extracts were prepared and subjected to an EMSA using radioactively labelled GR-response element as a probe. Where indicated, different amounts of bacterially purified GST or GST fusion proteins were added to the cell extracts. The fusion proteins consisted of GST alone or GST fused to either the wild-type RAP46 sequence (GST–RAP46) or RAP46 lacking the last 47 C-terminal amino acids (GST–RAP46dC47). (A) Inhibition of DNA binding by the GR is mediated by RAP46 and not RAP46C47. EMSA was carried out with cell extracts containing the GR and 1 µg GST, GST–RAP46 or GST–RAP46dC47. (B) Hsc70 relieves RAP46-mediated inhibition of DNA binding by the GR. COS-7 cells were transiently transfected with an empty expression vector (vector, lane 1), or an expression vector encoding either the GR (lanes 2–10) or an HA-tagged RAP46 (lanes 3–10). Whole-cell extracts were prepared and subjected to an EMSA using radioactively labelled GR response element as a probe. Where indicated, different amounts of purified Hsc70 were added to the whole-cell extracts. (C) Increased concentration of RAP46 downregulated DNA binding by the GR. Concentrations of GST–RAP46 ranging from 0.1 to 1000 ng was added to the cellular extract before the DNA binding reaction were carried out. (D) A RAP46–Hsc70 complex does not affect DNA binding by the GR. COS-7 cells were transiently transfected with either an empty expression vector (vector, lane 1) or an expression vector encoding the GR (lanes 2–5). Whole-cell extracts were prepared and subjected to EMSA. One microgram of bacterially produced GST (lanes 2 and 3) or GST–RAP46 fusion protein (lanes 4 and 5) were added to the cell extracts before providing the hormone and the probe. Where indicated, GST and GST–RAP46 were premixed with 2 µg of purified Hsc70 before addition to the cell extracts (lanes 3 and 5). In (A–D), dexamethasone (100 nM) was added to the EMSA reaction mixture prior to incubation with the radioactive probe.
