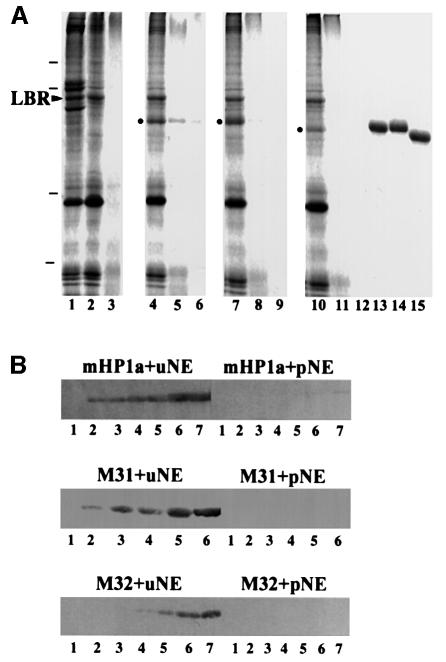
Fig. 6. Specific binding of HP1 proteins to isolated nuclear envelopes. (A) Binding of recombinant HP1 to isolated nuclear envelopes, as detected by SDS–PAGE and Coomassie Blue staining. Lane 1, whole nuclear envelopes (before urea extraction); lane 2, urea-stripped nuclear envelopes; lane 3, protease-digested nuclear envelopes; lane 4, urea-stripped nuclear envelopes plus GST–mHP1α; lane 5, protease-digested nuclear envelopes plus GST–mHP1α; lane 6, GST–mHP1α and buffer; lane 7, urea-stripped nuclear envelopes plus GST–M31; lane 8, protease-digested nuclear envelopes plus GST–M31; lane 9, GST–M31 and buffer; lane 10, urea-stripped nuclear envelopes plus GST–M32; lane 11, protease-digested nuclear envelopes plus GST–M32; lane 12, GST–M32 and buffer; lanes 13–15, profiles of the input GST–mHP1α, GST–M31 and GST–M32, respectively. Dashes correspond to molecular weight markers of 96, 68, 31 and 21 kDa. An arrowhead indicates the position of LBR. Dots indicate HP1 proteins that have bound to the membranes. (B) Binding of recombinant HP1 proteins to the nuclear envelopes, as detected by western blotting. The input was as follows: lanes 1, 0 µg; lanes 2, 0.5 µg; lanes 3, 1 µg; lanes 4, 2 µg; lanes 5, 4 µg; lanes 6, 8 µg; lanes 7, 16 µg. uNE and pNE correspond to urea-extracted and proteolyzed nuclear envelopes, respectively.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.