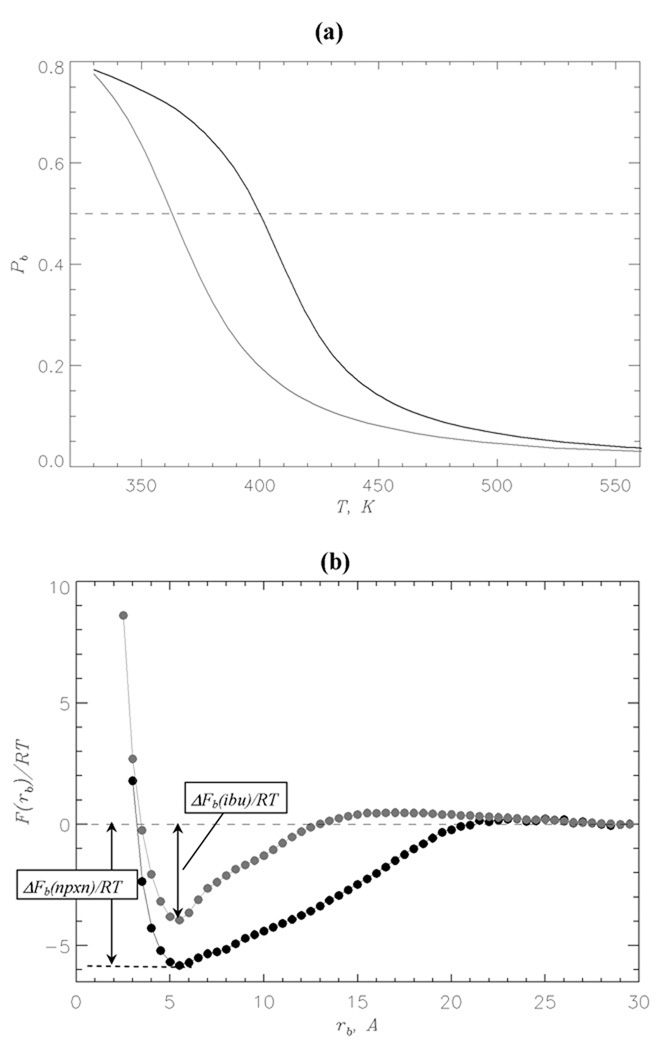
Fig. 2.
(a) Probability Pb(T) of binding of naproxen (in black) and ibuprofen (in grey) molecules to Aβ fibril as a function of temperature. Dashed line marks Pb = 0.5. (b) Free energy of ligand molecule F(rb) as a function of the distance rb between ligand and the surface of Aβ fibril at 360K: naproxen (in black), ibuprofen (in grey). The binding free energy is defined as ΔFb = Fb – F(rb = 30Å), where Fb is obtained by integrating over the states with F(rb) ≤ Fmin + 1.0RT and Fmin is the free energy minimum at small rb. The free energies at rb ≥ 30Å are set to zero. The figure shows that naproxen binds with higher affinity to the fibril than ibuprofen.