Table 3.
Antimalarial and antileishmanial activities of pyridinium oximes
| Entry | 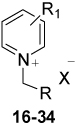 |
Antimalarial | Antileishmanial | Cytotoxicity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
P. falciparum |
L. donovani | Vero cells | ||||
| D6 Clone | W2 Clone | |||||
| IC50 µg/mL | IC50 µg/mL | IC90 µg/mL | IC50 ng/mL | |||
| 17 | R = CH2CH2CH2Br, R1 = 4-CONH2, X = Br |
3.7 (S.I. > 1.3) |
4.0 (S.I. > 1.2) |
na | na | nc |
| 21 | R = 5-bromothiophen-2-yl, R1 = 2-CHNOH, X = Cl |
na | na | 19 | 40 | nc |
| 24 | R = benzothiophen-3-yl, R1 = 2-CHNOH, X = Cl |
na | na | 18 | 40 | nc |
| Chloroquine | 0.015 | 0.12 | nt | nt | nt | |
| Artemisinin | 0.010 | 0.0065 | nt | nt | nt | |
| Pentamidine | nt | nt | 1.2 | 5 | nt | |
| Amphotericin B | nt | nt | 0.2 | 0.4 | nt | |
IC50, the concentration that affords 50% inhibition of plasmodial / leishmanial growth; IC90, the concentration that affords 90% inhibition of leishmanial growth; na, not active; nt, not tested; nc, Not cytotoxic; S.I., selectivity index = IC50 vero cells/IC50 P. falciparum.
