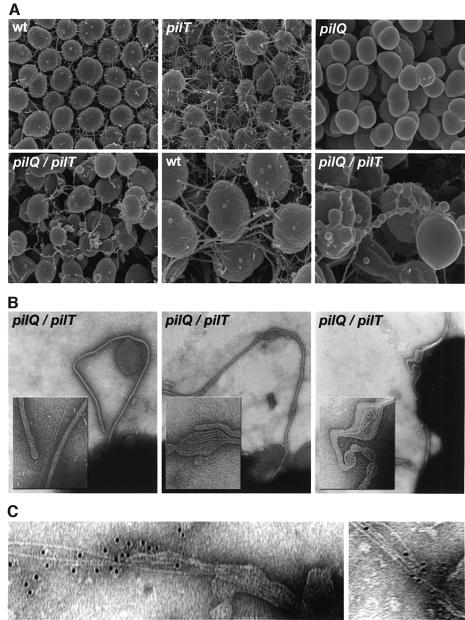
Fig. 2. Electron microscopic analysis of pilQ/pilT mutants shows altered cell surface structures comprised of membrane-bound pilus filaments. (A) Scanning electron micrographs of wild-type and mutant N.gonorrhoeae strains. wt (N400); pilT (MW4, pilTind); pilQ (GQ21, pilQ::mTncm21); pilQ/pilT (MW11, pilQ::mTncm21, pilTind). In the lower center and lower right panels, wt and pilQ/pilT micrographs are at 50 000× magnification; all others are at 25 000×. Individual N.gonorrhoeae cells are ∼1 µm in diameter. (B) Transmission electron micrographs showing membrane-bound pilus fibers in a pilQ/T mutant (strain MW11). Note that bulges seen in the membranous protrusions contain coiled fibers detected by TEM (center and right panels) and that they correspond to analogous structures seen in SEM. Micrographs are taken at a magnification of 90 000× and inset panels show digitally enlarged images at a 3× higher magnification. (C) Immunolabeling of fibers associated with disrupted blebs with antiserum raised against purified pili (135 000×).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.