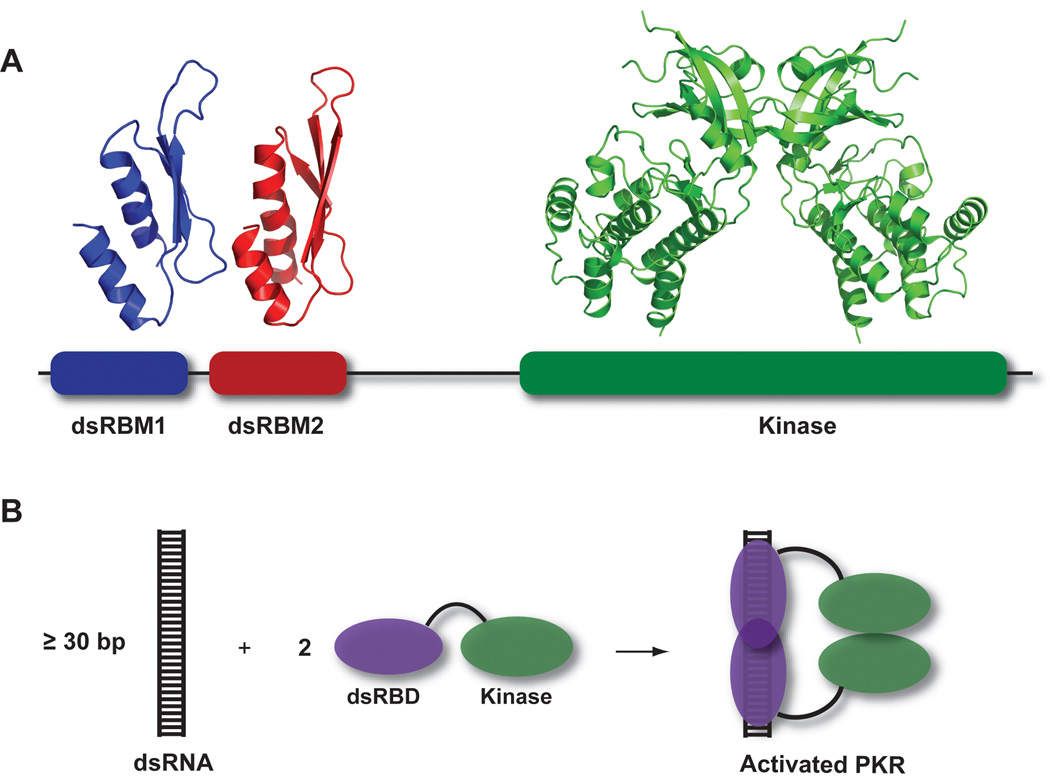
Figure 1.
Overview of PKR structure and function. A) PKR domain organization and structure. The N-terminal regulatory domain is comprised of two dsRNA binding motifs, dsRBM1 and dsRBM2 connected by an unstructured linker. Each of these motifs adopts the canonical αβββα fold in the NMR structure of dsRNA binding domain (PDB: 1QU6). In the crystal structure of a complex of the PKR kinase domain and eIF2α (PDB: 2A1A), the kinase domain has the typical bilobal structure observed in other eukaryotic protein kinases and dimerizes via the N-terminal lobe. B) Dimerization model for PKR activation by dsRNA. Binding to dsRNA induces PKR dimerization via the kinase domain, resulting in activation.