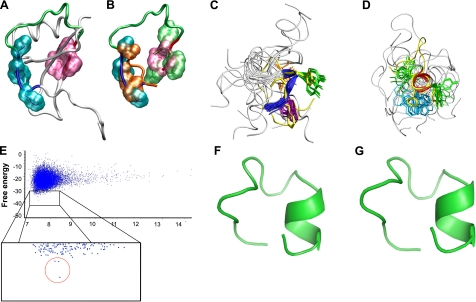
Figure 3.
Validation of the Rosetta abrelax algorithm on peptide R1.5G3 and modeling of new RANTES mimetics containing an in silico-optimized linker segment. A) NMR structure of full-length RANTES (11) shown by tube representation. The N- and C-terminal hydrophobic patches are highlighted as surfaces in turquoise and mauve, respectively. B) Manual superposition of the side chains of Phe12, Tyr14, and Ile15 (orange) and Tyr27, 1Nal28, and Tyr29 (green) from the average NMR structure of peptide R1.5G3 over their corresponding residues in full-length RANTES. C) Backbone atom superposition of the Phe12-Ile15 segment of the R1.5G3(Phe 28) model predicted by Rosetta over the corresponding residues from the average NMR structure of R1.5G3. The backbone of the N-terminal hydrophobic patch is shown as a blue tube for the R1.5G3 NMR structures and as a yellow tube for the Rosetta model. Side chains are shown as sticks. D) Backbone atom superposition of the Tyr27-Tyr29 segment of the R1.5G3(Phe 28) model predicted by Rosetta over the corresponding residues from the average NMR structure of R1.5G3. The backbone of the C-terminal hydrophobic patch is shown as a red tube for R1.5G3 NMR structures and as a yellow tube for the Rosetta model. Side chains are shown as sticks. Figure was generated using VMD. E) Scatterplot of free-energy levels of Rosetta-predicted models for a RANTES mimetic containing an in silico-optimized linker segment (Pro20→Thr and Ile24→Tyr), which yielded a stable helical motif at the C terminus. Results derive from the analysis of 11,000 models generated with the Rosetta abrelax protocol. Enlarged box shows a detail of the low-energy range with the 3 lowest energy models belonging to the same low-energy cluster, clearly segregated from all the other decoys, circled in red. F) Predicted structure of the lowest-energy model shown in E, containing an in silico-optimized linker segment. G) Predicted structure of peptide R2.0 (Phe28) containing the in silico-optimized linker segment as well as 2 additional mutations in the downstream residues (Lys25→His and Glu26→Asp). Model was predicted using the Rosetta standard design protocol. Figures were generated using PyMol 1.2 (http://www.pymol.org).