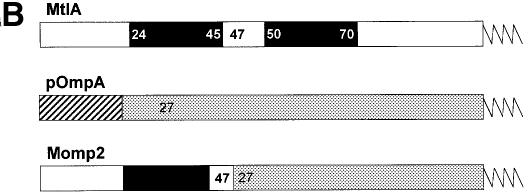
Fig. 1. Nascent chains of Momp2, a hybrid between the polytopic membrane protein MtlA and the secretory protein pOmpA, bind to both Ffh and trigger factor. (A) pOmpA, MtlA and Momp2 were synthesized in vitro by coupled transcription–translation of plasmids pDMB, p717MtlA-B and pMomp2, respectively. The addition of appropriate antisense oligodeoxynucleotides gave rise to a 125 amino acid N-terminal fragment of pOmpA (pOmpA-125), a 189 amino acid fragment of MtlA (MtlA-189) and a 146 amino acid fragment of Momp2 (Momp2-146). Co-synthesis of some full-length products (MtlA, OmpA and Momp2) was observed under these conditions. [35S]methionine-labeled translation products were precipitated with trichloroacetic acid (TCA), separated by SDS–PAGE (7–17% acrylamide) and visualized by phosphoimaging. Where indicated, Ffh (2 ng/µl) was present during synthesis. Cross-linking with DSS was followed by centrifugation through a sucrose cushion in a TLA-100.2 Beckmann rotor at 70 000 r.p.m. for 60 min at 4°C (Behrmann et al., 1998; Beck et al., 2000) and immunprecipitation (IP) using anti-Ffh and anti-trigger factor (TIG) antibodies. Molecular masses are indicated to the right. Cross-linking products with trigger factor (*) and Ffh (x) are indicated. (B) Construction of the hybrid protein Momp2 from MtlA and OmpA. For experimental details, see Materials and methods. Black boxes represent predicted transmembrane segments of MtlA (Sugiyama et al., 1991), with the preceeding and following amino acids each indicated in white. Numbering starts with the first N-terminal amino acid, with that of MtlA sequences given in bold. Only an arbitrarily long N-terminal part of each protein is drawn. The signal sequence of pOmpA is depicted as a hatched area, and the mature sequence as a gray box.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.