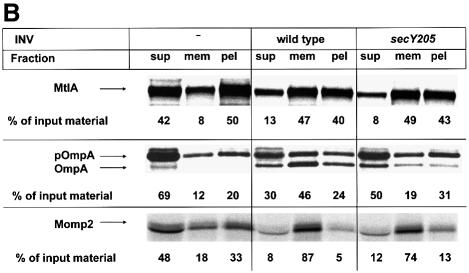
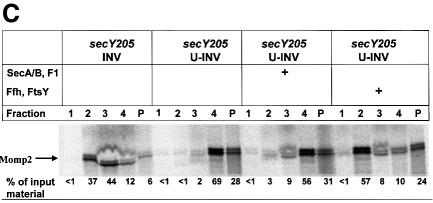
Fig. 3. Translocation of Momp2 requires a functional SecY–SecA interaction but not its membrane association. (A) pOmpA, MtlA and Momp2 were synthesized in vitro in the presence of INV buffer, wild-type INVs or secY205 INVs and the endogenous amounts of SecA, SecB, F1-ATPase, Ffh and FtsY. The percentage of translocation and integration was calculated by quantitation of the radioactivity measured in individual protein bands using phosphoimaging. The indicated percentage of OmpA translocation equals the ratio between radioactivity in the bands of pOmpA and OmpA after and before proteolytic digestion. The percentage of MtlA integration was calculated by the ratio between MtlA-MPF and MtlA, corrected for the loss of [35S]methionine residues during cleavage by proteinase K. The translocation of Momp2 equals the ratio between Momp2-MPF and Momp2. (B) As in (A), but membrane association was analyzed by subfractionation of the translation products on a two-step sucrose gradient. Radioactivity of the three subfractions was quantified and the sum set at 100%. (C) Flotation analyses of full-length Momp2 in the presence of secY205 INVs or secY205 U-INVs. In vitro synthesis of Momp2 was performed in the presence of the indicated components (see Figure 2 for the concentrations used) and the reaction mixture was subsequently separated by a flotation gradient centrifugation. Following centrifugation, 4 × 100 µl fractions were withdrawn from the top of the gradient and, after precipitation with TCA, separated by 15% SDS–PAGE. The pellet fraction was dissolved directly in loading buffer. Fractions 2 and 3 correspond to the membrane fraction.