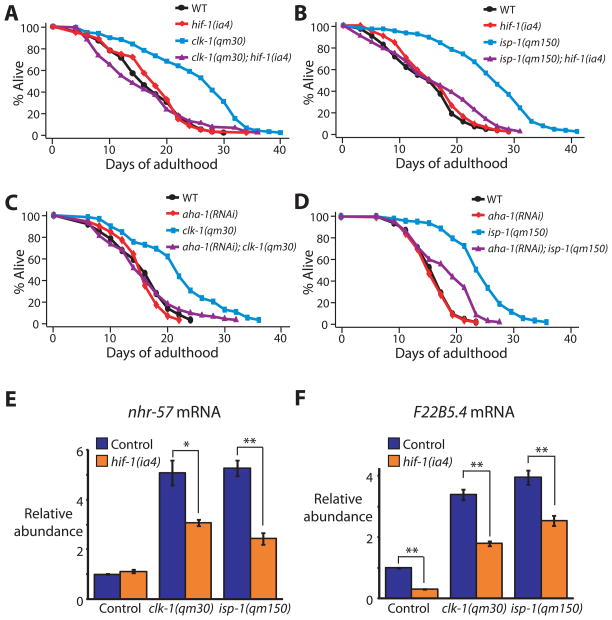
Fig. 2. The lifespan extension conferred by respiration mutants requires hif-1.
(A, B) hif-1(ia4) loss-of-function mutations decreased the longevity of clk-1(qm30) (A) and isp-1(qm150) (B) mutants significantly (in three out of four trials and four out of four trials, respectively; See Supplemental Table S2). (C, D) The long lifespan of clk-1(qm30) (C) and isp-1(qm150) (D) mutants was significantly shortened by aha-1 [HIF1β] RNAi. Neither the hif-1(ia4) mutation nor aha-1 RNAi affected the lifespan of wild type (WT). (See Supplemental Table S2 for statistical analysis.) [We note that whereas Mehta et al. and we both found that hif-1 mutations do not affect the lifespans of wild type [19], Chen et al. and Zhang et al. reported that hif-1 mutants live longer than wild type [37–38]. We carried out additional experiments to resolve this discrepancy, which are described in supplemental material (Fig. S2M, N)] (E, F) The increased mRNA levels of the HIF-1-dependent genes nhr-57 (E) and F22B5.4 (F) in clk-1(qm30) and isp-1(qm150) mutants were significantly decreased by hif-1(ia4) mutation. Error bars represent s.e.m (n=3, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, two-tailed Student’s t-test). See Fig. S2G, H for quantitative RT-PCR data of other hif-1-dependent hypoxia-inducible genes.