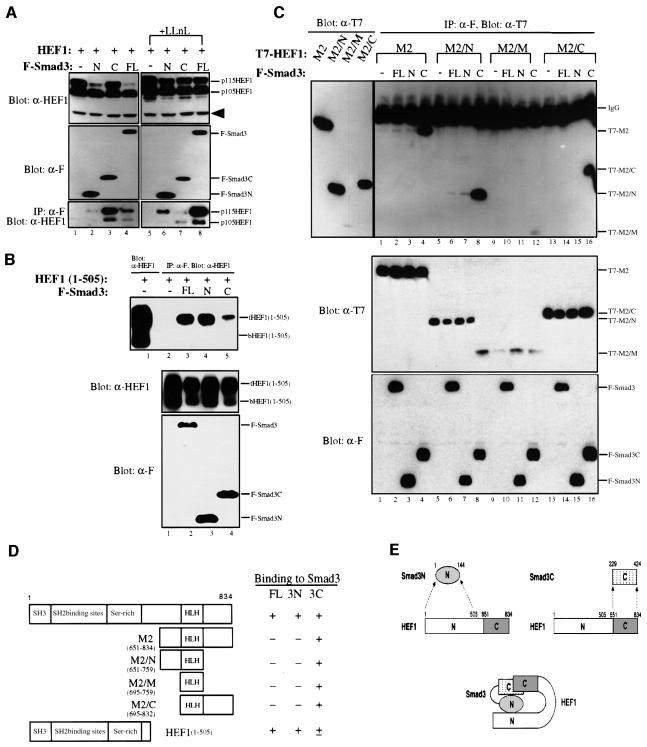
Fig. 3. Smad3 and HEF1 interact with each other through their N- and C-terminal domains. (A) Smad3 binds to HEF1 via both Smad3N (MH1) and Smad3C (MH2) domains, but only the N-terminal domain induces the degradation of HEF1. HEF1 was transfected alone or co-transfected with Flag-tagged full-length (FL), the N-terminal MH1 domain (N) or C-terminal MH2 domain (C) of Smad3 into 293 cells, untreated or treated with 50 µM LLnL for 9 h before harvest. Cell lysates were prepared and blotted with α-HEF1 and α-F antibodies (top and middle panels, respectively). Lysates were also immunoprecipitated with α-F antibody and blotted with α-HEF1 antibody (bottom panel). (B) The N-terminus of HEF1 preferentially binds to the Smad3 N-terminal domain. 293 cells were transfected with HEF1(1–505) alone or in combination with Flag-tagged full-length (FL), or the N- or C-terminal domains of Smad3. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with α-F antibody and blotted with α-HEF1 antibody (top panel, lanes 2–5). Lane 1 is the western blot for HEF1(1–505), which was expressed in two forms, designated as tHEF1(1–505) and bHEF1(1–505), respectively. Expression levels of HEF1(1–505) and Smad3 constructs are shown in the middle and bottom panels. (C) The C-terminus of HEF1 binds to the C-terminus of Smad3. T7-tagged HEF1 deletion constructs were transfected alone or co-transfected with Flag-tagged full-length (FL), or the N- or C-terminal domains of Smad3 into 293 cells. For the top panel, lysates were immunoprecipitated with α-F antibody and blotted with α-T7 antibody to detect the co-immunoprecipitation of HEF1 subdomains with Smad3 subdomains (lanes 1–16). Expression of the HEF1 subdomains was detected by western blotting in the left panel to serve as the molecular weight markers for the right panel. The protein levels of the transfected constructs in each lysate were monitored by western blotting using α-T7 and α-F antibodies, respectively (middle and bottom panels). (D) Summary of the HEF1 deletion constructs used in (C) and the result of the domain-mapping studies. (E) A cartoon that illustrates the mutual interaction between Smad3 and HEF1. Smad3 and HEF1 interact with each other through their N- and C-terminal domains.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.